Unit 4
Key Marketing Dimensions
Q1) Write a small note on marketing ethics. (5 marks)
A1) Marketing ethics is an area of applied ethics which deals with the moral principles behind the operation and regulation of marketing. It seeks to market honesty, fairness, and responsibility altogether advertising. Standards for marketing ethics guide companies in their efforts to try to "the right thing." These standards help identify acceptable practices, foster control, and deal honestly and fairly with customers. They also ensure businesses suit the law. Sometimes companies develop and publish their own ethical standards; other times they suit the regulations or guidelines of their professional or industry associations. Marketing ethics sets out a framework permanently practice in marketing, no matter the product or market sector. Ethical marketing describes an approach to marketing during which companies set high ethical standards and communicate those positively. A tobacco company that avoided advertising would be complying with marketing ethics. An organization that sourced environmentally friendly products from a country or company that practiced excellent employee relations would be practicing ethical marketing. The principles of marketing ethics are-
• All marketing communications share the common standard of truth.
• Marketing professionals abide by the very best standard of personal ethics.
• Advertising is clearly distinguished from news and entertainment content.
• Marketers should be transparent about who they pay to endorse their products.
• Consumers should be treated fairly based on the character of the product and therefore the nature of the buyer (e.g., marketing to children).
• The privacy of the buyer should never be compromised.
• Marketers must go with regulations and standards established by governmental and professional organizations.
• Ethics should be discussed openly and honestly during all marketing decisions.
For example,
The Hindu: Parliamentary Behavior
This is a good addon to the examples of ethical advertisements in India. A class opens to a debate with the teacher’s instruction to maintain strict parliamentary behavior by the groups involved. What follows is both funny and sad— the students create a ruckus within the classroom— from pulling at each other’s hair to throwing books. The background score of Indian classical music does a cathartic job of driving home the point, and the tagline follows:
- Behave Yourself, India.
- The Youth Are Watching.
Nestle: Good Food, Good Life
Being a global trade association, Nestle places a high value on its public relations by catering to the demography and homogenous customer base.
Q2) Discuss the unethical marketing practices in India. (10 marks) (2018)
A2) Avoiding unethical marketing practices can also help a business avoid other consequences, like losing the great faith and loyalty of consumers, and jeopardizing profitability. The worst practices of the bunch are:
- Misleading statements
Misleading statements can land a business in legal trouble. The law expects advertising claims to be supported by evidence, which proved to be a tricky standard for a number of cigarette manufacturers once they originally promoted their products as being “healthy.” actually, not all claims are provable, and this is often where some marketers deliberately plan to blur the road with exaggerated claims and puffery, which are other kinds of unethical marketing. Consumers may turn a deaf ear to a product that claims to be “the best,” and that they are known to disdain marketing that promises to “transform their life” or “make them the envy of all their friends.” Distorting facts to intentionally confuse or mislead consumers. A classic example: stamping a product as sugar- or calorie-free when it does actually contain some sugar and calories, or touting a product as “healthy” when it's loaded with carbohydrates and sodium.
2. Making false or deceptive comparisons:
A number of rival products much more prevalent 20 years ago among general consumer products, you still might see this happen within the tech sector. (Think smartphones.) Competition tends to be fierce when rivals resort to side-by-side comparisons. And consumers may find such how helpful, as long because the information is accurate and truthful.
3. Inciting fear or applying unnecessary pressure:
“Limited time offers” are notorious for the latter, which is ok if a deadline really exists and thus the tone doesn't sound threatening.
4. Exploiting emotions or a news event:
Such instances happen every once during a short time, then make a quick exit when consumers complain about feeling manipulated.
5. Stereotyping
Stereotyping or depicting women as sex symbols merely to draw attention to a product. "While it would be intuitive to use models in adverts for beauty products and cosmetics, having half-naked models in adverts for generators, heavy machinery, smartphones and other products not strongly associated with women are both nonsensical and unethical,” says Profitable Venture.
6. Disparaging references
Disappearing references to age, gender, race or religion. Many professional comics have learned the hard way that the road between humour and bad taste are often painfully thin it would be easier to determine if the humour packs an insult or a put-down that produces you grimace.
7. Doctoring photos or using photos that are not authentic representations:
Most of the people expect professional photographers and videographers to make the most of lighting and close-ups. But the finished products should be accurate depictions that are free of touch-ups and other enhancement techniques that are designed to mislead.
8. Plagiarizing a competitor:
For a small-business owner discovering that a competitor has copied or impinged on a tagline, blog post or promotion are often painful – or infuriating. The reality is, plagiarism probably happens more often than most businesspeople will ever know, because of the online.
9. Spamming or sending unsolicited emails to potential customers:
The FTC allows a business one such opportunity then, a business violates the CAN-SPAM act. In effect since 1993, the act also prohibits false or misleading header information and deceptive subject lines.
10. Distortion of facts to mislead or confuse potential buyers
This is another common unethical marketing practice. A typical example is when a food processing company claims that its products are sugar-free or calorie-free when indeed they contain sugar or calories. Such a company is only trying to mislead potential buyers, since they are unlikely to buy the products if it is made known that they contain sugar or calories.
11. Bad-mouthing rival products
Emphasizing the dark sides of your rival’s products in a bid to turn potential customers towards your own products is another common but unethical marketing practice. Rather than resort to this bad strategy, you should emphasize on those aspects that make your offer stand out from the rest of the pack. That’s professional and ethical.
12. Concealing dark sides or side effects of products or services
This unethical marketing practice is rife in the natural remedies industry, where most manufacturers deceive potential buyers that their products have no side effects because they are “made from natural products”.
Q3) What role is played by consumer organisations regarding marketing ethics? (5 marks) (2018, 19)
A3) Functions performed by consumer organizations and non-government organizations are as follows:
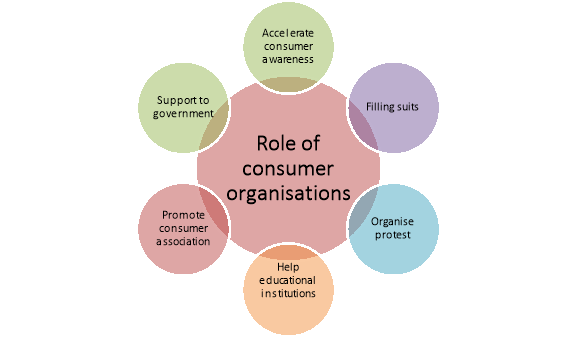
Figure: Role of consumer associations
(1) Accelerating Consumer Awareness/Educating Consumers:
The first priority of a consumer organization is to accelerate consumer awareness towards their rights. To accomplish this task following efforts are made:
(i) To publish brochures, journals and monographs.
(ii) To rearrange conferences, seminars and workshops.
(iii) To teach consumers to assist themselves.
(iv) To supply education to women about consumerism.
(v) To encourage to follow desirable consumption standards.
(2) Collecting Data on Different Products and testing them:
These organisations collect samples of various products from time to time and test them. Then the results of the tests are declared to public. During this way, these organisations provide prior information to consumers about the authenticity of product and protect them aside from this; these organisations also add conducting investigation/ research on consumer’s problems.
(3) Filing Suit on Behalf of Consumers:
Whenever a consumer fails to boost his voice of protest regarding his complaints, these consumers’ organisations come to his rescue and file a case within the court. By rendering this service to the consumers, the consumers get a way that they are not alone in their struggle. They also run voluntary complaint centres for the guidance of consumers.
(4) Organising Protests against Adulteration etc.:
The consumers’ organisations play an enormous role in eliminating the evils of adulteration, hoarding, black- marketing, and under-weight selling. Whenever there's an unnecessary rise within the costs of certain things, the consumers’ organization raise a voice of protest against it. Consumer organisations prepare films and cassettes associated with adulteration in food products, ill effects of medicines and Acts related to consumer protection. Many a times exhibitions are arranged to bring awareness among the consumers against spurious and adulterated products. Nowadays consumer organisations are playing a significant role in encouraging consumers to spice up their voice against faulty and inferior products.
(5) Helping Educational Institutions:
These organisations tell the tutorial institutions the way to prepare courses of study keeping in sight the interests of the consumers. They stress the very fact that a special article on consumers’ interest should be added to the courses on general study.
(6) Promoting Network of Consumer Associations:
Consumer organisations attempt to grow their numbers they need to hide all the regions of the country so as those buyers of all the regions are benefited by their services. Their effort is to form a federation at the apex level then through the medium of the federation reach state and district level.
(7) Extending Support to Government:
Consumer organisations by informing the govt. Agencies about adulteration, artificial scarcity, inferior quality products and other such evils help the govt. This successively helps the govt.to conduct proceedings in time.
Q4) What are the strategies adopted by competitive market leader. (5 marks) (2018)
A4) The leader firm might become weaker or old-fashioned against new entrants also as existing rival firms. It firm can use one or a mix of three strategies to retain its leadership. Market leader strategies are discussed below-
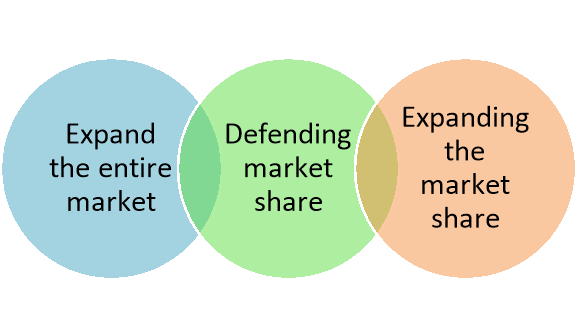
Figure: Market leader strategies
1. Expand the entire market:
Market leader firms can normally gain the utmost when the entire market expands the main target of expanding the entire market depends on where the product is in its life cycle. This strategy is usually used when a product is within the maturity stage. As an example, the Japanese increased their car production to enter new countries. Market leaders can look for new users, new uses, and more usage of its products when the product is within the maturity stage of the product life cycle. ICICI Bank, as an example, entered into rural banking and agriculture business financing when it felt the heat of competition within the overcrowded and super-saturated urban market. Maruti Udyog started True Value car division—used cars certified by Maruti engineers—to expand their market within the rural and concrete markets well.
2. Defending market share:
When the leader tries to expand the entire market size, it must also continuously defend its current business against enemy attacks as an example, Coca-Cola must constantly maintain its guard against Pepsi-Cola. Similarly, Hero Honda should constantly maintain its guard against Bajaj, Honda, Suzuki and TVS within the two-wheeler market during this strategy, the leader firm must keep its costs down, and its price must be according to the worth that customers see within the product. There are six ways during which a market might use to guard its market position:
(i) Position defense:
This strategy involves allocating maximum resources into the present successful brands. To beat a foothold defense an attacker therefore typically adopts an indirect approach rather than the head-on attack that the defender expects. As an example, HUL increased its ad-spend on Clinic Plus and Sun silk shampoos and gave heavy promotions through discount.
(ii) Flanking defense:
This strategy both guards the market position of leading brands and develops some flank market niches to function a defensive corner either to protect a weak front or to determine an invasion base for counterattack, if necessary. a perfect example is how HUL successfully nourished its first Rs.100 crore Indian-made brand Vim during a competitive dish wash market. It had been able to check the attack of competitors through product innovation, attractive public campaigns, road shows and PR.
(iii) Pre-emptive defense:
This defense strategy man oeuvre involves the launching of an offence against an enemy before it starts an offence. As an example, Titan launched more brands and sub-brands to corner the market share of HMT watches within the first 1990s.
(iv) Counter offensive defense:
This is a technique of identifying a weakness in an attacker and aggressively going then market niche so on cause the competitor to drag back its efforts to defend its own territory. When a leader is attacked, he may base his counterattack within the attacker’s territory. The attacker has to deploy resources to the present territory for defense. When CEAT tyres attacked TVS Srichakra in Tamil Nadu markets, TVS decided to expand its coverage to Ceat tyre’s hub within the north and west of India through innovative campaigns like road rallies, road shows and attractive public campaigns.
(v) Mobile defense:
This strategy involves the leader broadening and expanding its territories to new market areas by diversifying. The leader takes innovation works in both these directions. As an example, a five-star hotel can become a distant exchange dealer, inbound and outbound tour operator, flouriest then on. Such diversification into related areas comes under mobile defense strategies.
(vi)Contraction defense:
This strategy involves retrenching into areas of strength and is typically utilized in later stages of a product life cycle or when the firm has been under considerable attack. As an example, HUL decided to consider its core business areas, that is, soaps and detergents, and has emerged because the clear leader within the rest room industry.
3. Expanding the market share:
Market leaders can improve their profitability by increasing their market shares, like HUL, Procter and Gamble, McDonald’s and Titan. Last, market leaders who stay top have learned the art of expanding the entire market, defending their current territory, and increasing their market share and profitability. Competing with highly aggressive market leaders presents a formidable challenge to all or any or any newcomers. Take the case of the tea or coffee industry. No newcomers dare enter in to the market because the top brands of Tata, HUL, and Nestle guard their share so successfully.
Q5) What are the strategies adopted by market challenger. (5 marks) (2019)
A5) A market challenger is a firm that has a market share below that of the market leader, but enough of a presence that it can exert upward pressure in its effort to gain more control.
The strategies of market challenger are-
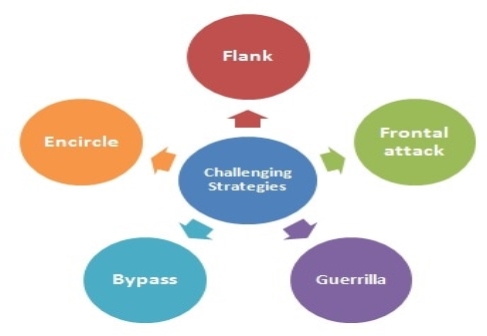
Figure: strategies of market challenger
1) Use a frontal attack
Observed most prominently within the smartphone market today, or more commonly within the Pepsi vs Coca Cola war since ages, a frontal attack is seen when a competitor attacks another based on the strengths of the competitor. Example – Pepsi introduces Diet Pepsi when Coke introduces Diet coke. Both have strength of product expansion and a various product portfolio. So, during an immediate frontal attack, Pepsi also launches a product in response to its market challenger.
2) Flank attack
The above example of Pepsi and coke contains 2 brands which are very strong within the FMCG market and have no other competitor. Thus, they use frontal attacks but what if a little player has to combat a mammoth. Then the player uses a flank attack and attacks the competition supported its weaknesses. Example – Many technology firms like AMD vs Intel, Apple vs Microsoft, et al. Operate the idea of Flank attack.
3) Encirclement attack
This form of market challenger strategy is employed when the competitor attacks another on the thought of strengths also as weaknesses and doesn't leave any stone unturned to overthrow the competition. The current E-commerce scenario is that the simplest example of the encirclement attack where the E-commerce companies are ready to go negative in their margins to beat a competitor on turnover basis. They have to return on top and gain maximum customers by hook or crook.
4) Bypass attack
It just by passed it. There's often no simpler example of the Bypass attack kind of market challenger strategy this kind of strategy is found during a firm which has the brains to innovate. And when it innovates, it bypasses the entire competition and creates a segment of its own off course, other competitors soon follow. But the attack is extremely useful within the future to form brand reputation and gain customers. For example, Samsung bypass Nokia etc.
5) Guerrilla marketing
Making small but useful changes, which repeatedly puts your brand within the forefront, and slowly but surely makes it an enormous name within the market, is that the crux of Guerrilla marketing. A little brand, which wants to require on huge competitors, which first become famous during an area market, then will introduce price discounts and trade discounts. Slowly but surely, the name of the tiny player will spread and it will then use branding activities and ATL and BTL marketing activities. Over a period of your time, the tiny player has become a successful large player and should be a thorn within the side for all major players within the market. Take the AJE group as an example. They launched their flagship product “Big cola” several years back within the sell was slowly so successful, that the brand is now present in multiple countries.
Q6) What are the strategies adopted by market follower. (5 marks) (2018)
A6) A market follower is a company that follows what the leader in its sector does. A market follower does not like taking risks, i.e., it is the opposite of a maverick. Instead, it waits and observes what its competitors do, especially the market leader. It then only adopts the leader’s successful strategies. The rule of business is that when you're a market leader, there are definitely getting to be market followers. Many companies begin with a market follower strategy. In fact, in today’s world, the competency of all companies is so high that innovation is quickly copied or imitated in several formats. For example, Apple came out with the multi touch smart phones, but today Samsung is leading that market in terms of total turnover. Thus, there are several market follower strategies in effect in today’s business environment. Market followers are sure to exist during a mature market. The market followers are wider just in case of online marketing because online marketing has lower entry barriers and better returns. Thus, in online commerce itself, you will see that companies like Snapdeal, Flipkart, Amazon, Jabong have all started one after the opposite. Off course, the market leaders were Ebay and Amazon. But they're facing stiff competition nowadays.
The market follower strategies are-
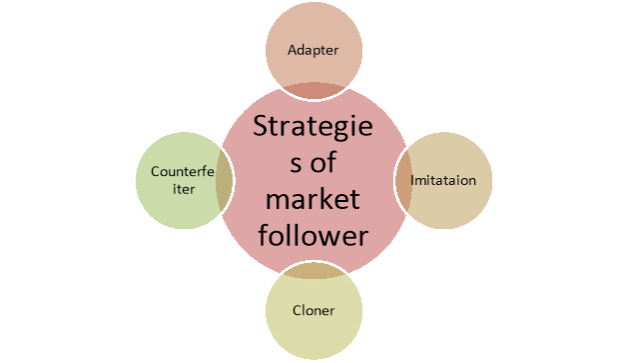
Figure: Strategies of market follower
1) Adapter
Adapter is white collared market follower strategy. Automobiles use the difference sort of market follower strategy. Cars like Maruti 800, Alto, Zen, brio, etc are all adapters which they adapt the only qualities from each other by changing the design of the car. Similarly, there are technology adapters a bit like the Dell laptop and Sony Vaio laptop. These market followers have similar products but they struggle to adapt from their closest competition. Adapters can soon become leaders also because they're going to adapt, learn and make a much better product than the higher competition.
2) Imitation
Imitation is that the simplest kind of flattery. But such a flattery can cause a large dent in your profit margins if you are a product manufacturer. Imitators make use of your hard-earned brand equity and provide a product which has similar characteristics as yours, albeit at a lower cost. The difference might be that the new product is made from poor material or that it doesn't have the service or promise that your brand offers. Nonetheless, there is a huge marketplace for imitators where people want to shop for products at lower cost as they can’t afford the upper one. For example are often the imitation of Tata sky, where Tata sky is that the market leader and brought digital TV revolution to India but was soon imitated by Videocon, Airtel, Reliance et al.
3) Cloner
There is a bright side between an imitator and a cloner. An imitator might copy variety of your product qualities, but it maintains its own product qualities also as an example – timesjobs.com is an imitator of naukri.com, on the opposite hand times jobs has its own unique product characteristics also. The next time you're in Bangkok, plan to get the clones of Samsung phones.
4) Counterfeiter
The best example of counterfeiting is selling the originals via piracy. Where cloning involves manufacturing of slightly altered products, counterfeiting involves thieving and should be a black market follower strategy. The simplest example is pirated DVDs and CDs of flicks and music. If you notice, time and time again the film industry wakes up against piracy. This is often actually because piracy and counterfeiting steal their work. Similarly, you will find shoes from Reebok and Adidas also as numerous other products within the market which are counterfeited.
Q7) Define rural marketing. Discuss the features of rural market. (12 marks) (2018)
A7) Rural marketing is a process of developing, pricing, promoting, and distributing rural specific goods and services leading to desired exchange with rural customers to satisfy their needs and wants, and also to achieve organizational objectives. The concept of Rural Marketing in India Economy has always played an influential role within the lives of individuals. In India, leaving out a number of metropolitan cities, all the districts and industrial townships are connected with rural markets. The concept of rural marketing in India is typically been found to forms ambiguity within the mind of individuals who think rural marketing is all about agricultural marketing. However, rural marketing determines the completing of business activities bringing within the flow of goods from urban sectors to the rural regions of the country also because the marketing of various products manufactured by the non-agricultural workers from rural to urban areas. Rural marketing in Indian economy is often classified under two broad categories-
i. The market for trade goods that comprise of both durable and non-durable goods
Ii. The market for agricultural inputs that include fertilizers, pesticides, seeds, and so on.
In rural marketing, a firm possesses to undergo marketing efforts to satisfy rural segments, which notably differ from urban segments in some aspects. At the same time, we must note that increasing literacy rate, improved sources of income, awareness because of improved and increased means of communication and transportation, high rate of mobility within and between countries because of liberalization and globalization, and lots of other such reasons, some customers are likely to be identical.
Examples of Rural Marketing
1. HDFC Bank’s “Festive Treats” and “Har Gaon Hamara” Rural Campaigns
2. “Experience Hyundai” Campaign by Hyundai
3. “Khushion Ki Doli” by Hindustan Unilever Ltd (HUL)
4. “Accessibility” Campaign by Coca-Cola
5. “UTSAV” Campaign by Asian Paints
6. Dabur’s “Nauchandi Mela” and “700 Se 7 Kadam” Campaigns
The following images shows rural marketing campaigns-
The main reason why the companies are that specialize in rural market and developing effective strategies is to tap the market potential which can be identified as follows:
1. Large and scattered population:
Consistent with the 2001 census, 740 million Indians forming 70 per cent of India’s population live in rural areas. The speed of increase in rural population is additionally greater than that of urban population. The agricultural population is scattered in over 6 lakhs villages. The rural population is extremely scattered, but holds an enormous promise for the marketers.
2. Higher purchasing capacity:
Purchasing power of the rural people is on rise. Marketers have realized the potential of rural markets, and thus are expanding their operations in rural India. In recent years, rural markets have acquired significance in countries like China and India, because the general growth of the economy has resulted into substantial increase in purchasing power of rural communities.
3. Market growth:
The rural market is growing steadily over the years. Demand for traditional products like bicycles, mopeds and agricultural inputs; branded products like toothpaste, tea, soaps and other FMCGs; and durables like refrigerators, TV and washing machines has also grown over the years.
4. Development of infrastructure:
There is development of infrastructure facilities like construction of roads and transportation, communication network, rural electrification and public service projects in rural India, which has increased the scope of rural marketing.
5. Low standard of living:
The standard of living of rural areas is low and rural consumers have diverse socio-economic backwardness. This is often different in several parts of the country. A consumer during a village area features a low standard of living because of low literacy, low per capita income, social backwardness and low savings.
6. Traditional outlook:
The rural consumer values old customs and traditions. They're doing not prefer changes. Gradually, the rural population is changing its demand pattern, and there is demand for branded products in villages.
7. Marketing mix:
The urban products cannot be dumped on rural population; separate sets of products are designed for rural consumers to suit the rural demands. The marketing mix elements are to be adjusted consistent with the requirements of the rural consumers.
Q8) Discuss the strategies of effective rural marketing. (8 marks)
A8) An appropriate segmentation of the highly heterogeneous rural market and identification of the requirements and works of varied segments will form the very basis for rural market strategies. For rural market, it'll be ideal to think about strategies from the marketing mix point of view main strategies are associated with product, price, place and promotion. The strategies of effective rural marketing are-
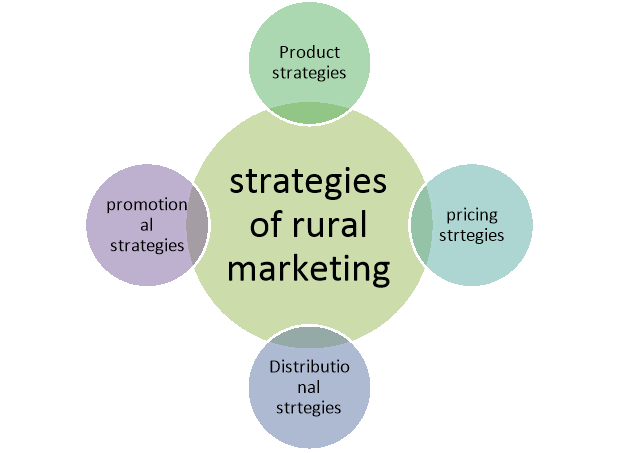
Figure: Strategies for rural marketing
A. Product Strategies
Meaningful product strategies for rural market and rural consumers are discussed here.
1. Small unit and low priced packing
Larger pack sizes are out of reach for rural consumers thanks to their price and usage habits. This method has been tested by other products like shampoos, biscuits, pickles, vicks five gram tins, etc. In the strategy of keeping the low priced packed the target is to stay the value low in order that the entire rural community can do this won't be possible altogether kinds of products, but wherever this may be resorted to, the market is certain to expand.
2. New product designs
A close observation of rural household items indicates the importance of redesigning or modifying the products. The manufacturing and marketing men can think in terms of latest product designs specially meant for rural areas keeping their lifestyles in sight.
3. Sturdy products
Sturdiness of a product either in terms of weight or appearance is a vital fact for rural consumers. The product meant for rural areas should be sturdy enough to face rough handling and storage. People in rural areas like bright flashy colors like red, blue, green etc., and feel that products with such colors are sturdy but they're more concerned with the utility of the item also.
4. Brand name
The rural consumers are more concerned with the utility of the products. The brand name awareness within the rural areas is fairly high. A brand name and/or logo is extremely essential for rural consumers for it are often easily remembered.
B. Pricing strategies
Pricing strategies are considerably linked to product strategies. A number of these strategies are mentioned here.
1. Low cost/cheap products
This is a common strategy being adopted widely by many manufacturing and marketing men. Price is usually kept low by small unit packings.
2. Avoid sophisticated packing
Simple package is often adopted which can bring down the value because it is presently being done in the case of biscuits. Some innovation in packing technology is extremely necessary for rural markets.
3. Refill packs/reusable packaging
Such measures have an enormous impact on the rural market. By such technology also the price is often reduced. Additionally, the packaging material used should preferably lend itself for reuse in rural areas. A perfect example during this direction is often the packing of fertilizers. Now companies have started packing fertilizers in LDPE or HDPE sacks, which are not only tamper proof but also reusable.
4. Application useful engineering
This is how which can be tried to evolve cheaper products by substituting the costly raw material with the cheaper one, without sacrificing the standard or functional efficiency of the product, as an example in food industry, ‘soya protein is getting used rather than milk protein. Milk protein is dear while soya protein is cheaper but the nutrition value is same. This method yields itself for application in many engineering or product designed areas so as that the value is often kept at a reasonable level. These areas got to be explored by manufacturing and marketing men within the context of rural markets. The pricing strategy for rural market will depend upon the scope for reducing the worth of the product to suit the rural incomes and at an equivalent time not compromising with the utility and sturdiness of the market.
C. Distribution strategies
Most manufacturers and marketing men do have a distribution arrangement for village with a population of a minimum of 5000 people. While it's -essential to formulate specific strategies for distribution in rural areas, the characteristics of the product, its period of time and other factors got to be kept in mind. The distribution strategies that are specifically designed for rural areas are: through co-operative societies, public distribution system, multi-purpose distribution centres, distribution up to feeder markets/mandi town’s shanties/hat/jathras/melas, agricultural input dealers etc. Experience has shown that the cooperatives have played a useful role in improving the marketing services within the regulated markets. The fact, however, remains that these societies command only a touch share of the entire markets and do not present any challenge to the private trade at in most places. The Gujarat Cotton Cooperative Marketing Societies set a good example of vertically integrated markets. The cooperative marketing institutions got to introduce scale economies in their marketing operation and provide efficient and comparable services to the purchasers in competition with the private trade. Cooperative institutions would do better if the state level marketing federations enter into multilevel activities to reinforce the turnover of their business. The non-governmental organizations can anchor a key role in awakening the rural people to form into cooperatives highlighting the possible benefits without being exploited.
D. Promotion strategies
Mass media could also be a strong medium of communication. It'd be television, cinema, medium, radio then on the opposite means of mass media available are hoardings/wall paintings, shanties/hats/melas, non-price competition, special campaigns etc. Besides these, other mass media like hand bills and booklets, posters, stickers, banners of the schemes etc. For disseminating the data, associated with agricultural and other rural industries products, the govt. Should circulate pamphlets either to Panchayati raj office or to schools where it is often documented for the reference. While making efforts to reinforce the marketing system within rural areas and thus the marketing of rural produce to other areas, we should always foresee the forces of globalization affecting the market forces.
Q9) Write a brief note on digital marketing. (8 marks) (2019)
A9) Digital marketing is that the utilization of the web, mobile devices, social media, search engines, and other channels to succeed in consumers. Some marketing experts consider digital marketing to be a completely new endeavour that needs a replacement way of approaching customers and new ways of understanding how customers behave compared to traditional marketing. Digital marketing targets a selected segment of the customer base and is interactive. Digital marketing is on the increase and includes search result ads, email ads, and promoted tweets – anything that comes with marketing with customer feedback or a two-way interaction between the company and customer. Internet marketing differs from digital marketing. Internet marketing is advertising that's solely on the web, whereas digital marketing can happen through mobile devices, on a subway platform, during a video game, or via a smartphone app. In the parlance of digital marketing, advertisers are commonly mentioned as sources, while members of the targeted ads are commonly called receivers. Sources frequently target highly specific, well-defined receivers. It targeted shift workers and travellers with digital ads because the company knew that these people made up an outsized segment of its late-night business. McDonald's encouraged them to download a replacement Restaurant Finder app, targeting them with ads placed at ATMs and gas stations, also as on websites that it knew its customers frequented at night.
For example, Social Media Marketing (SMM)
Search Engine Optimisation (SEO)
Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
Email Marketing.
Marketing Automation.
Digital Advertising.
Content Marketing.

Trends in Digital Marketing
Some of the current trends in digital marketing are-
1. Going LIVE and interesting through videos:
They dominated Facebook, Instagram and YouTube. Even a social media video app tik tok took the youth segment of tier 2 & 3 cities by its fascination.
All a testimony to how our audience loves consuming content on video. Seeing this, brands are increasing their share on digital marketing spends too. Because videos also increase 53X likelihood of getting your website on the first age of search results. And as an improvement on them, the Facebook live and Instagram live are where these visitors are spending more of their time. These live videos are watched 3X longer than the videos on the feed because they provide the audience an option to invite information and feedback in real time.
2. Strong on social media
Majority of the marketers think that social media goes to be big as compared to apps or web. It's especially going to be vital for the sake of brand awareness and brand connectivity. And to help the brands achieve these goals, social media channels keep undergoing evolution. New features are constantly added to Instagram, YouTube etc. One such trend is of shoppable posts, which is becoming a huge a part of the Instagram audience says that they are discovering products of latest brands on Instagram something to tap within the upcoming year.
3. Catching them on the go
As the audience gets busier and their attention span decreases, more content would be consumed in transit. The Omni channel approach across video sites, social media, OTT players and digital OOH placements in transit – OLA Play etc. will increases. This also spells rapid growth in hyper –locally relevant digital OOH like at restaurants, malls, railway stations and bus stands.
4. Amazon the marketing channel
Owing to its being the product search start line and rich customer data, amazon is merely estimated to grow further as a marketing channel of its own. It’s estimated that Google are getting to be putting huge efforts into servicing and increasing the share of its product searches.
5. AI everywhere:
Several Al features already add the background of social media platforms. From, auto recommendation to image recognition, Al will only work on empowering these social media platforms further. Whereas on websites, Al and machine learning – powered chatbots are found making it easier for the visitors to communicate with them. In upcoming years smoothening customer service through Al would become a priority.
Q10) Write a brief note on green marketing. (8 marks) (2018, 19)
A10) Green marketing is that the marketing of environmentally friendly products and services. It's becoming more popular as more people become concerned with environmental issues and chooses that they need to spend their money during how that's kinder to the earth. Green marketing can involve variety of various things, like creating an eco-friendly product, using eco-friendly packaging, adopting sustainable business practices, or focusing marketing efforts on messages that communicate a product’s green benefits. This type of selling is often costlier, but it can also be profitable because of the increasing demand. As an example, products made locally in North America tend to be costlier than those made overseas using cheap labour, but they have how smaller carbon footprint because they don’t get to fly across the planet to urge here for a couple of consumers and business owners, the environmental benefit outweighs the price difference. Everything you'd prefer to realize green marketing. The term green marketing came into prominence within the late 1980s and early 1990s.
Importance of green marketing
Importance of green marketing are highlighted below-
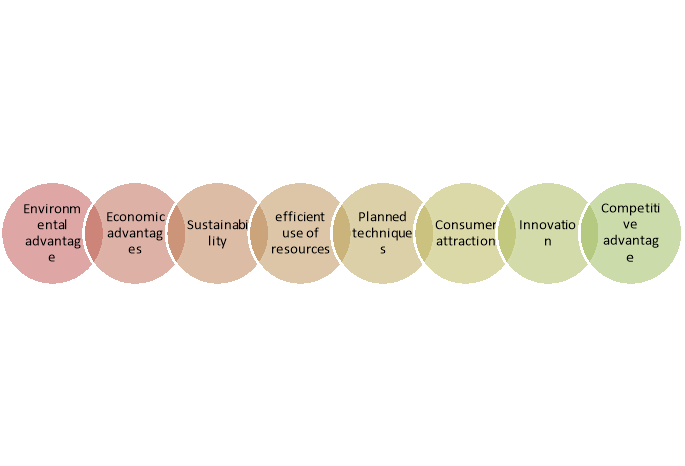
Figure 6: Importance of advertising
1. Environmental Advantages:
Going green is an environmentally responsible choice. It's estimated that 40 per cent of all greenhouse gases within us comes from energy production that businesses use to heat, cool and light workplaces. Reducing these energy needs reduces CO2 output, helping to regulate heating. As businesses use more natural resources than individual consumers, recycling business materials and conserving water contribute to conservation on a bigger scale.
2. Economic Advantages:
The reduction in waste equals lower operating costs and more savings. Eco-friendly business equipment and practices like – low-wattage or LED lights, use of natural lighting, water conservation policies, mandatory recycling and hybrid company vehicles economize on utilities, fuel and office supplies. This generates instant income. Further going green puts a business during a positive light within the eyes of customers, potential investors, distributors, activists, watchdog groups, communities and prospective employees.
3. Sustainability:
Going green is about sustainability; this sustainability translates to sustainable profits in green sectors with secure futures. The future-safe markets include biomaterials, green buildings, personal transportation, smart grids, mobile applications and water filtration.
4. Efficient Use of Resources:
Today, human demands and desires are unlimited but resources are short enough that can't fulfill the human needs. Markets need to facilitate the consumers by utilizing resources efficiently.
5. Planned Techniques:
It must develop strategically techniques and innovative policies to understand the organizational goals effectively with none wastage of some time and other resources. Green marketing examples of different products and services develops a growing interest among customers throughout the world.
6. Consumer Attraction:
Green marketing samples of various products attracts the consumers regarding environment protection. People are such a lot conscious about their environment and variations in behavior. Green marketing is taken into account as growing marketing that helps to style socially and sustainable products.
7. Innovation:
Green marketing helps to style such kinds of products that are economically affordable and satisfy the human needs efficiently. It produces innovative green products that consume less resource.
8. Competitive Advantage:
Companies enjoy competitive advantage over other companies within the market through green marketing examples. Today, companies which adopt green marketing techniques gain more competitive advantage over other companies which are not conscious about such techniques and environment. Companies which develop innovative products and services with innovative qualities at affordable rates are successful within the market. Green marketing could also be a gaggle of activities that are designed to satisfy the consumer’s demands.