Question Bank of Module 01
Q-Explain the shape of d orbital.
Shape of d orbital:
The magnetic orbital quantum number for d orbitals is given as (-2,-1,0, 1,2). Hence, we can say that there are five d-orbitals. These orbitals are designated as dxy, dyz, dxz, dx2–y 2 and dz2. Out of these five d orbitals, shapes of the first four d-orbitals are similar to each other, which is different from the dz2 orbital whereas the energy of all five d orbitals is the same.

Q- Enlist the rules that should be obeyed for the electron distribution.
The maximum number of electrons in any main energy level (shell) is given by, ‘2n2’, where, n is an integer and representing the “principal quantum number”. For different main energy levels the value of ‘n’ and maximum number of electrons are given in table below-
Sl. No. | Energy level or Orbit (shell) | Principal quantum number ‘n’ | Maximum Number of electrons (2n2) |
1 | K | 1 | 2×12 = 2 |
2 | L | 2 | 2×22 = 8 |
3 | M | 3 | 2×32 = 18 |
4 | N | 4 | 2×42 = 32 |
Q-Using complete subshell notation (no abbreviations), predict the electron configuration of each of the following atoms:
- C
- P
- V
- Sb
A- C- 1s2 2s2 2p2
P-1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3
V-1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2
Sb- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p3
Q-Explain LCAO.
The approximate method used to represent molecular orbital is called as the Linear Combination of Atomic Orbital. It is a quantum superposition of atomic orbital and a technique for calculating molecular orbital in quantum chemistry.
Rules for the Linear Combination of Atomic Orbital are:-
- The combining atoms should have the same symmetry along the molecular axis for proper combination. e.g. All the sub-orbitals of 2p have same energy but still, the 2pz orbital of an atom can only combine with a 2pz orbital of another atom but cannot combine with 2px and 2py orbital as they have a different axis of symmetry.
- The two atomic orbital will combine to form molecular orbital. Greater is the extend of overlap of atomic orbital; greater will be the nuclear density.
The combining atomic orbital must be of equal energy or approximately same energy.
Q- Which atom has the electron configuration:
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d2 ?
A- Zr
Q- Explain Bonding and Anti Bonding Molecular Orbital.
Bonding Molecular Orbitals
When addition of wave function takes place, the type of molecular orbitals formed are called Bonding Molecular orbitals and is represented by
ΨMO = ΨA + ΨB.
They have lower energy than atomic orbitals involved. It is similar to constructive interference occurring in phase because of which electron probability density increases resulting in formation of bonding orbital. Molecular orbital formed by addition of overlapping of two s orbitals. It is represented by s.
Anti-Bonding Molecular Orbitals
When molecular orbital is formed by subtraction of wave function, the type of molecular orbitals formed are called Antibonding Molecular Orbitals and is represented by
ΨMO = ΨA - ΨB.
They have higher energy than atomic orbitals. It is similar to destructive interference occurring out of phase resulting in formation of antibonding orbitals. Molecular Orbital formed by subtraction of overlapping of two s orbitals. It is represented by s* (*) is used to represent antibonding molecular orbital) called Sigma Antibonding. Therefore, Combination of two atomic orbitals results in formation of two molecular orbitals, bonding molecular orbital (BMO) whereas other is anti-bonding molecular orbital (ABMO).
Q-Draw the Molecular Orbital Diagram of Be2.
Be2 Electronic Configuration :- 1S2 2S1
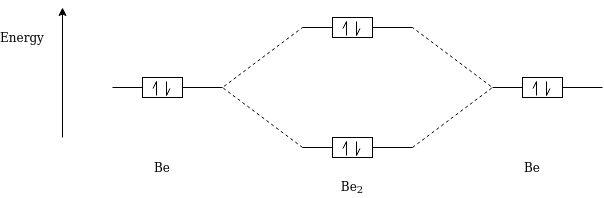 Magnetic Property : Diamagnetic in Nature
Magnetic Property : Diamagnetic in Nature
Bond Order :- 1/2(Nb-Na)
= 1/2(2-2)
=0
Q- Draw the molecular diagram of O2 and its magnetic property.
O2 Molecule:-
Electronic Configuration:-
O2 => σ1S2 σ*1S2 σ2S2 σ*2S2 π2Px2 π2Py2 π*2Px1 π*2Py1

Bond Order= ½ [Nb-Na]
=1/2 [8-4]
=2
Magnetic Property= Paramagnetic Character
Q- Draw the molecular diagram of CO.

Q-Which of the following atoms would be expected to form negative ions in binary ionic compounds and which would be expected to form positive ions: Br, Ca, Na, N, F, Al, Sn, S, Cd?
Anions: Br, N, F, S,
Cations: Ca, Na, Al, Sn (because it's a metal), Cd (because it is a metal)