Unit – 4
Sales Report
Q1)Explain sales report.
A1)
Sales report
The fundamental purpose of sales reports is to provide information about the activities of the salesperson. It serves as a control mechanism, as the management gets the needed information about sales people’s performance in the field. They can compare with targets assigned and can determine the success rate of their sales person.
A good sales reporting system assists not only the management in exercising control but it can even help sales personnel in their self-improvement. Recording sales performance in a written form forces an individual salesperson to check their own work. They become their own critics, and self-critics is often more valuable and effective than others. This motivates sales person to improve coordination of their efforts with sales management plans and the management process functions more smoothly.
Purpose of Sales Reports
General purpose of sales report is to provide information for measuring performance. Additional purposes are
1. To provide data for evaluating sales person’s performance: these reports provide details concerning account and prospects called on, number of calls made, orders obtained, days worked, miles travelled, selling expenses etc.
2. To help the sales person plan their work: the salesperson could plan his future work with innovative ideas and measures on the basis of past sales reports.
3. To record customer’s suggestions and complaints: sales reports helps record customer’s suggestions and complaints and their reactions to new products, service policies, policies change, advertising campaigns and so forth.
4. Gathering information: sales reports helps in gathering competitive activities, new products, market test, change in promotion policy, product policy, price policy etc.
5. To report changes in local business and economic conditions.
6. To provide information requested by marketing research data on dealer’s sales inventories and competitive products.
7. To keep the mailing list updated for promotional and catalogue material.
TYPES OF SALES REPORTS
1. Progress or call report: most companies have a progress or call report system. It is prepared individually for each call and for all calls made daily or weekly. Progress report keep management informed about the salespersons activities. It provides important data to the company about calls made by salespersons in different territories. Accordingly, the company could inform and suggest the salespersons about revisits. Usually the call report contains more detailed information such as the class of customer, other brand likings of customer, etc.
2. Expense Report: Most companies prepare expense report for reimbursement and income tax purposes. From sales management point of view, the purpose of preparing expense report is to control the nature and amount of expenses made by salespersons.
3. Sales Work Plan: a sales work plan is a work plan submits by salesperson giving details about prospect to be contacted, products to be discussed, routes to be travelled etc.
4. Potential new business report: This reports informs about prospects who may become source of new business. It provides data for evaluating the extent and effectiveness of work done the salesperson.
5. Lost sales report: This provides information for evaluating salesperson abilities to keep customers and keep customer and sell against competition. Lost sales reports provide the way to needed sales training, change in customer services policies and product improvement reason for the loss of the business.
6. Report of complaint and /or adjustment: this report provides information for analyzing complaints arising from a salesman’s work, complaint by class of customer and cost of complaint adjustment. This assists management in in detecting needed product improvements and changes in merchandising and service practice policies.
Q2) Explain sales manual.
A2)
Sales manual
One of the fastest ways to increase sales of product is to educate the sales force on the key features and benefits of the product, unique advantages of the product, how to sell the product, and the competition.
Performance of the company depends on its sales team’s performance and capabilities. That’s why smart companies keep sales teams highly informed about all things essential, relevant and helpful to being “smart” and effective. They supply every resource the sales team needs to do the job exceptionally well, and keep them well trained.
The sales manual is part policy, part procedures, part best practices, part how-to guide. It explains protocols and processes. It provides standards of performance.
In all cases, conciseness and good organization of sales manual is important because sales people don't have much time to read and they need quick access to the information. It is essential that the sales manual is concise provide quality information.
Some features of a sales manual are as follows
1. Accurate and up to date.
2. Relevant.
3. Easily accessed.
4. Readily available.
5. Secure.
6. Readily understood.
7. Easy to read and well organized.
Online of a sales manual
- Contact information: Let the sales person know where they can get more information on product or on any part of the guide. Include email addresses and phone numbers.
- Selling strategies: Outline target market, market size, sales cycle, ideal customer profile, list of current customers, references, press mentions and success stories. If this is a onepage sales guide the information must be kept to one paragraph with a few bullets.
- Products and Demonstration: Positioning of the product, how it fits into the overall product line, a list of key features and benefits, demonstration highlights, most common customer questions, and product updates. For a one page sales guide use only the top three the key features and benefits.
- Competition: A table of competitors with a feature matrix is the best way to show this information. Don't forget to include pricing. Short write-ups on key competitors including strengths, weaknesses, and an overview of their strategy can be useful if you have just a few competitors. Since many competitors fall into similar categories you may want to outline a more broad strategies for competing against competitors in those categories. You may also want include write-ups of what the competitors will be saying to your customers.
- Pricing: Include all pricing, ordering, and configuration information.
- Collateral Documents: All associated collateral including datasheets, brochures, and white papers.
- Sales presentation: It is important to let the sales people know how to present the product. An online presentation detailing high-level positioning, success stories, and features and benefits with a script is great. A video of the presentation is also a useful tool.
- Glossary: You may need a glossary of terms and acronyms associated with the product.
- Index: Include an index if the sales manual is over 50 pages.
- Reference Material: Include reference where the sales persons could find more information. Like Annual Report of the company, monthly booklets, circulars etc.
Essential of an effective sales manual
1. Eye Catching Format: as no one is going to read the entire manual, it is important that the required information is presented and eye-catching manner. There should proper table of contents, clear headings for each sections and subsections, index and glossary terms. Use of diagrams, tables and illustrations be made to summarize complex information.
2. Concise length: the length of the document will vary depending upon the target audience and the nature and number of product options.
3. Pronunciation: a new salesperson might be unfamiliar with the buzz words of the specific industry. Pronunciation must be called out wherever necessary and in glossary terms.
4. Well marked customer sections: sales people will often copy parts of the sales manual and handover it to customers. Sections of the manual must be clearly identified.
5. Consistent updates: a sales guide out of date is useless. An updated sales manual keeps the salesperson informed about the developments within the company and new competitive announcements.
Q3) Explain order book.
A3)
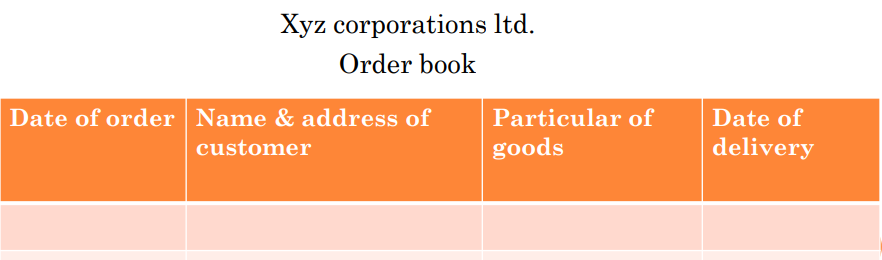
An Order Book is a business’s list of open, unshipped, customer orders, normally time-phased and valued at actual individual order prices. This is also referred as sales order book. Sales order is the order placed by the buyer and maintained in the books of seller. Therefore, sales order book contains the details of sales order, order reference number order amount etc.
This book contains the details of sales order, the seller and vendors name, sales order number, voucher number, voucher type, order reference number, order amount etc
Specimen of Sales order book
Q4) Explain cash memo.
A4)
Cash memo
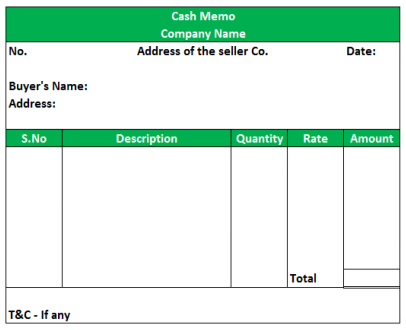
Cash Memo is a commercial document issued by the seller to the purchaser when cash is received as a payment. When a trader sells goods for cash, he gives a cash memo and when he purchases goods for cash, he receives a cash memo. Details regarding the items, quantity, rate and the price are mentioned in the cash memo. It works as a proof of cash payment made.
In simple words, we can say that a Cash memo is a document stating cash received for goods sold. It is a paid bill for cash sales
A cash memo usually contain the following:
- Name and address of supplier.
- Name and address of purchaser.
- Serial number & date.
- Customer/purchase order number.
- Description of goods.
- Rates and total amount.
- Discount.
- Tax details.
- Total amount in words and figures.
Q5) Explain tour diary.
A5)
Tour diary
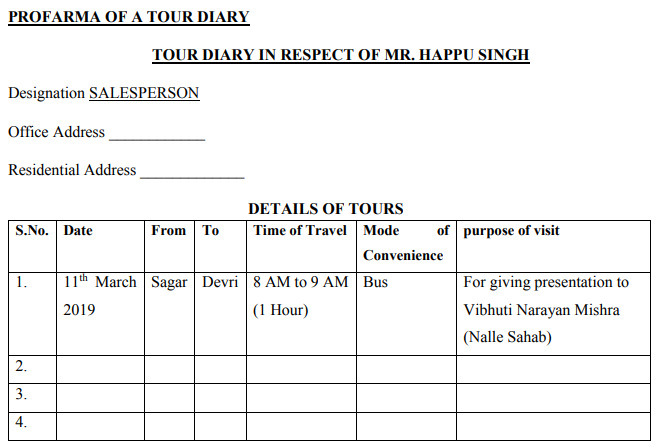
Tour diary is a document containing information about a salesman visit to various places for selling purpose. Every salesman has to give detailed account of his visits. The tour diary must include information about name of visited place, purpose of the visit, name of the person contacted with, date and time, mode of convenience etc.
A tour diary helps a company informed about movement of salesperson, there regularity and it also shows their dedication towards work. A salesman consistently visiting various places for qualifying and identifying prospects, gathering information about prospects, giving presentations to the prospects is considered a valuable asset for the company. Tour diary is also helpful in measuring efforts and performances of a salesman.
It may contain the following information:
- Names of places visited(cities/states/country)
- Dates on which visit is made
- Mode of transport used
- Expenses incurred on travel
- Names and details of prospective customer
- Result of visits in terms of order, feedback etc.
Q6) Explain ethical aspects in selling.
A6)
Ethics refers to a set of moral principles dealing with what is right or wrong. These principles govern most of actions of individuals and organizations. Ethics is very important in businesses. In context of personal selling where one to one interaction and relationship building is necessary, ethics plays a major role in sustaining such relationship.
Many people enjoy working in sales because of the autonomy to make decisions, make deals, and satisfy customers. However, with freedom comes the responsible to act in ethical ways. Salespersons are likely to face ethical dilemmas. Most of the times salespersons work in the field unnoticed and unsupervised. There is no one to keep a check on their activities, whether they are doing working ethically or not. Some of the ethical activities could be with regard to company and some could be with regard to customers. Salespersons might report inaccurate working hours, inflate sales data and number of calls made. Also, they might provide information to customer in order to close the sale.
Ethical issues from company’s Perspective
- Misusing companies credit card and expense account: a salesperson must use credit card only for sales purposes and not for personal purposes. Many salesperson use credit card for dinner, see a show or stay a hotel, bringing spouse or friend on a business trip without permission. The company loses money when a salesperson attaches receipts of money spent on person purpose.
- Reporting Inaccurate working hours: salesman get freedom in their working as there is no close person to supervise them in their field work. So, salesperson do not provide actual hours worked but inflate their working hours.
- Inflate the number of contact calls: since nobody is watching, the salesperson can exaggerate the number of calls he made, so that he looks busier than other salespersons.
- Misusing confidential information: salespersons usually have access to important and confidential information about the company’s policies, products and services.
- Unauthorized discounts: it has been observed that on many occasions, to meet their targets and increase sales, salespersons provide unauthorized discounts to customers. This kind of practice results in unnecessary price cutting and company has to bear the ultimate loss.
- Unethically joining competitors or quitting the job without proper notice: A company spends a lot time, money and efforts in recruiting and training the salespersons. Such trained salespersons are generally in huge demand and competitive firms may attract them by offering higher amount of salary. It is unethical If a salesperson quits the job by getting such offer and joins other firm and shares secret information about the company,
- Stealing the leads and clients of other competitor: there is a cut throat competition prevailing in the market resulting in sales person’s stealing competitor’s customers and converting them into their customers. Such practices are unethical and unprofessional from the business perspective.
Ethical issues from Customers Perspective
1. Making false exaggerated claims: a salesperson must not make false and exaggerated claims in order to make sales in case they do not have the complete information asked by the customer, they need not lie and request customer to give them some time to look for it.
2. Not entertaining customer’s complaints properly: handling complaints is not an easy task. Many a times salespersons do not respond to customers queries and complaints whole heartedly. The customer is not satisfied then it may result in loss of valuable customer by the company.
3. Special treatment or discrimination between customers: Ideally, all customers should be treated equally and should be offered equal incentives. But, in practically, sales person tends to favor some customers, give them extra incentives or discounts. This is an unfair practice; salespeople avoid such practices.
4. Hiding essential information from customers: The salespersons hide essential information about the negative features of the product. None of the product can be picture perfect, if there are some weaknesses, it’s always better to bring it to the notice of customer with meaningful justification.
5. Forceful selling or pressure tactics: in order to persuade the customer to purchase the product, the salesperson create artificial scarcity of the product and use pressure techniques to compel the customer to purchase the product.
6. Misleading pricing or fake discounts: if the product price is not clearly mentioned on the pack, the sales person has the tendency to charge different prices from different customer. They might even inflate the price or give fake discounts to customers and play with their innocence.
7. Ineffective after sales services: effective after sales services is necessary to create good relationship with customers so that customers get satisfied and remain loyal to the company. It has been observed that in various situations, before selling the product, the salesperson promises various benefits and after sales service, but once the product is sold they do not fulfil their commitment to the customers.
Factors effecting ethics in personal selling
Individual Factors:
1. Age: since age is associated with length of time in a person’s career, experienced sales persons have been found to be more concentrated toward careful conduct of their responsibilities and are less involved in unethical sales activities.
2. Gender: Reports or studies shows women are more ethical in them in their selling behavior compared to men.
3. Personal Values: Personal Values of a person largely affects ethics in salespersons behavior. Many a time, salespersons learned values since childhood determines his behaviors on field.
Organizational Factors
1. Selecting, Hiring and Training: if the company is careful while recruiting, hiring and training the individuals, there will be less issues of unethical behaviors.
2. Companies Code of ethics: code of ethics in an organization largely affects the behavior of salespersons. If the company has a strong code of ethics, there will be less chances of ethical conflicts in behaviors of sales people.
3. Supervision and discipline: While managing ethics, supervisors should have a close look at the behavior of salesperson. The supervisor/sales manager himself follow discipline in his own actions as his actions directly affects and influences the actions of salesforce.
4. Reward and Punishment Policies: reward and punishment policies also affect the ethical behaviors of salesperson. If the punishment policy is harsh, the salespeople will not repeat unethical behaviors in future.
Q7) Explain types of sales report.
A7)
Sales report
The fundamental purpose of sales reports is to provide information about the activities of the salesperson. It serves as a control mechanism, as the management gets the needed information about sales people’s performance in the field. They can compare with targets assigned and can determine the success rate of their sales person.
A good sales reporting system assists not only the management in exercising control but it can even help sales personnel in their self-improvement. Recording sales performance in a written form forces an individual salesperson to check their own work. They become their own critics, and self-critics is often more valuable and effective than others. This motivates sales person to improve coordination of their efforts with sales management plans and the management process functions more smoothly.
Purpose of Sales Reports
General purpose of sales report is to provide information for measuring performance. Additional purposes are
1. To provide data for evaluating sales person’s performance: these reports provide details concerning account and prospects called on, number of calls made, orders obtained, days worked, miles travelled, selling expenses etc.
2. To help the sales person plan their work: the salesperson could plan his future work with innovative ideas and measures on the basis of past sales reports.
3. To record customer’s suggestions and complaints: sales reports helps record customer’s suggestions and complaints and their reactions to new products, service policies, policies change, advertising campaigns and so forth.
4. Gathering information: sales reports helps in gathering competitive activities, new products, market test, change in promotion policy, product policy, price policy etc.
5. To report changes in local business and economic conditions.
6. To provide information requested by marketing research data on dealer’s sales inventories and competitive products.
7. To keep the mailing list updated for promotional and catalogue material.
TYPES OF SALES REPORTS
1. Progress or call report: most companies have a progress or call report system. It is prepared individually for each call and for all calls made daily or weekly. Progress report keep management informed about the salespersons activities. It provides important data to the company about calls made by salespersons in different territories. Accordingly, the company could inform and suggest the salespersons about revisits. Usually the call report contains more detailed information such as the class of customer, other brand likings of customer, etc.
2. Expense Report: Most companies prepare expense report for reimbursement and income tax purposes. From sales management point of view, the purpose of preparing expense report is to control the nature and amount of expenses made by salespersons.
3. Sales Work Plan: a sales work plan is a work plan submits by salesperson giving details about prospect to be contacted, products to be discussed, routes to be travelled etc.
4. Potential new business report: This reports informs about prospects who may become source of new business. It provides data for evaluating the extent and effectiveness of work done the salesperson.
5. Lost sales report: This provides information for evaluating salesperson abilities to keep customers and keep customer and sell against competition. Lost sales reports provide the way to needed sales training, change in customer services policies and product improvement reason for the loss of the business.
6. Report of complaint and /or adjustment: this report provides information for analyzing complaints arising from a salesman’s work, complaint by class of customer and cost of complaint adjustment. This assists management in in detecting needed product improvements and changes in merchandising and service practice policies.
Q8) Explain online of a sales manual.
A8)
Sales manual
One of the fastest ways to increase sales of product is to educate the sales force on the key features and benefits of the product, unique advantages of the product, how to sell the product, and the competition.
Performance of the company depends on its sales team’s performance and capabilities. That’s why smart companies keep sales teams highly informed about all things essential, relevant and helpful to being “smart” and effective. They supply every resource the sales team needs to do the job exceptionally well, and keep them well trained.
The sales manual is part policy, part procedures, part best practices, part how-to guide. It explains protocols and processes. It provides standards of performance.
In all cases, conciseness and good organization of sales manual is important because sales people don't have much time to read and they need quick access to the information. It is essential that the sales manual is concise provide quality information.
Some features of a sales manual are as follows
1. Accurate and up to date.
2. Relevant.
3. Easily accessed.
4. Readily available.
5. Secure.
6. Readily understood.
7. Easy to read and well organized.
Online of a sales manual
- Contact information: Let the sales person know where they can get more information on product or on any part of the guide. Include email addresses and phone numbers.
- Selling strategies: Outline target market, market size, sales cycle, ideal customer profile, list of current customers, references, press mentions and success stories. If this is a onepage sales guide the information must be kept to one paragraph with a few bullets.
- Products and Demonstration: Positioning of the product, how it fits into the overall product line, a list of key features and benefits, demonstration highlights, most common customer questions, and product updates. For a one page sales guide use only the top three the key features and benefits.
- Competition: A table of competitors with a feature matrix is the best way to show this information. Don't forget to include pricing. Short write-ups on key competitors including strengths, weaknesses, and an overview of their strategy can be useful if you have just a few competitors. Since many competitors fall into similar categories you may want to outline a more broad strategies for competing against competitors in those categories. You may also want include write-ups of what the competitors will be saying to your customers.
- Pricing: Include all pricing, ordering, and configuration information.
- Collateral Documents: All associated collateral including datasheets, brochures, and white papers.
- Sales presentation: It is important to let the sales people know how to present the product. An online presentation detailing high-level positioning, success stories, and features and benefits with a script is great. A video of the presentation is also a useful tool.
- Glossary: You may need a glossary of terms and acronyms associated with the product.
- Index: Include an index if the sales manual is over 50 pages.
- Reference Material: Include reference where the sales persons could find more information. Like Annual Report of the company, monthly booklets, circulars etc.
Essential of an effective sales manual
1. Eye Catching Format: as no one is going to read the entire manual, it is important that the required information is presented and eye-catching manner. There should proper table of contents, clear headings for each sections and subsections, index and glossary terms. Use of diagrams, tables and illustrations be made to summarize complex information.
2. Concise length: the length of the document will vary depending upon the target audience and the nature and number of product options.
3. Pronunciation: a new salesperson might be unfamiliar with the buzz words of the specific industry. Pronunciation must be called out wherever necessary and in glossary terms.
4. Well marked customer sections: sales people will often copy parts of the sales manual and handover it to customers. Sections of the manual must be clearly identified.
5. Consistent updates: a sales guide out of date is useless. An updated sales manual keeps the salesperson informed about the developments within the company and new competitive announcements.
Q9) Explain ethical issues from company’s perspective.
A9)
Ethical issues from company’s Perspective
- Misusing companies credit card and expense account: a salesperson must use credit card only for sales purposes and not for personal purposes. Many salesperson use credit card for dinner, see a show or stay a hotel, bringing spouse or friend on a business trip without permission. The company loses money when a salesperson attaches receipts of money spent on person purpose.
- Reporting Inaccurate working hours: salesman get freedom in their working as there is no close person to supervise them in their field work. So, salesperson do not provide actual hours worked but inflate their working hours.
- Inflate the number of contact calls: since nobody is watching, the salesperson can exaggerate the number of calls he made, so that he looks busier than other salespersons.
- Misusing confidential information: salespersons usually have access to important and confidential information about the company’s policies, products and services.
- Unauthorized discounts: it has been observed that on many occasions, to meet their targets and increase sales, salespersons provide unauthorized discounts to customers. This kind of practice results in unnecessary price cutting and company has to bear the ultimate loss.
- Unethically joining competitors or quitting the job without proper notice: A company spends a lot time, money and efforts in recruiting and training the salespersons. Such trained salespersons are generally in huge demand and competitive firms may attract them by offering higher amount of salary. It is unethical If a salesperson quits the job by getting such offer and joins other firm and shares secret information about the company,
- Stealing the leads and clients of other competitor: there is a cut throat competition prevailing in the market resulting in sales person’s stealing competitor’s customers and converting them into their customers. Such practices are unethical and unprofessional from the business perspective.
Q10) Explain ethical issues from customers perspective.
A10)
Ethical issues from Customers Perspective
1. Making false exaggerated claims: a salesperson must not make false and exaggerated claims in order to make sales in case they do not have the complete information asked by the customer, they need not lie and request customer to give them some time to look for it.
2. Not entertaining customer’s complaints properly: handling complaints is not an easy task. Many a times salespersons do not respond to customers queries and complaints whole heartedly. The customer is not satisfied then it may result in loss of valuable customer by the company.
3. Special treatment or discrimination between customers: Ideally, all customers should be treated equally and should be offered equal incentives. But, in practically, sales person tends to favor some customers, give them extra incentives or discounts. This is an unfair practice; salespeople avoid such practices.
4. Hiding essential information from customers: The salespersons hide essential information about the negative features of the product. None of the product can be picture perfect, if there are some weaknesses, it’s always better to bring it to the notice of customer with meaningful justification.
5. Forceful selling or pressure tactics: in order to persuade the customer to purchase the product, the salesperson create artificial scarcity of the product and use pressure techniques to compel the customer to purchase the product.
6. Misleading pricing or fake discounts: if the product price is not clearly mentioned on the pack, the sales person has the tendency to charge different prices from different customer. They might even inflate the price or give fake discounts to customers and play with their innocence.
7. Ineffective after sales services: effective after sales services is necessary to create good relationship with customers so that customers get satisfied and remain loyal to the company. It has been observed that in various situations, before selling the product, the salesperson promises various benefits and after sales service, but once the product is sold they do not fulfil their commitment to the customers.
Q11) Explain order book and cash memo.
A11)
Order book
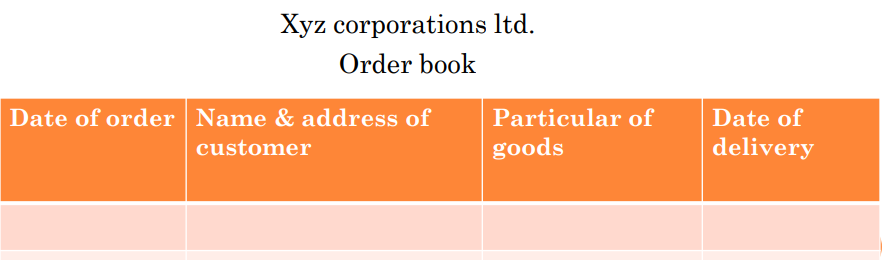
An Order Book is a business’s list of open, unshipped, customer orders, normally time-phased and valued at actual individual order prices. This is also referred as sales order book. Sales order is the order placed by the buyer and maintained in the books of seller. Therefore, sales order book contains the details of sales order, order reference number order amount etc.
This book contains the details of sales order, the seller and vendors name, sales order number, voucher number, voucher type, order reference number, order amount etc
Specimen of Sales order book
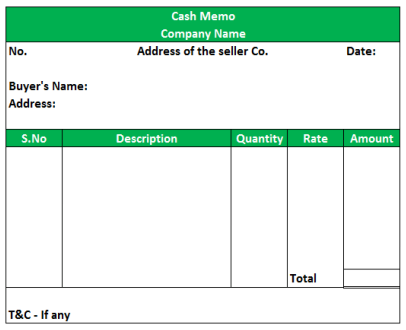
Cash memo
Cash Memo is a commercial document issued by the seller to the purchaser when cash is received as a payment. When a trader sells goods for cash, he gives a cash memo and when he purchases goods for cash, he receives a cash memo. Details regarding the items, quantity, rate and the price are mentioned in the cash memo. It works as a proof of cash payment made.
In simple words, we can say that a Cash memo is a document stating cash received for goods sold. It is a paid bill for cash sales
A cash memo usually contain the following:
- Name and address of supplier
- Name and address of purchaser
- Serial number & date
- Customer/purchase order number
- Description of goods
- Rates and total amount
- Discount
- Tax details
- Total amount in words and figures
Q12) Explain purpose and types of sales report.
A12)
Sales report
The fundamental purpose of sales reports is to provide information about the activities of the salesperson. It serves as a control mechanism, as the management gets the needed information about sales people’s performance in the field. They can compare with targets assigned and can determine the success rate of their sales person.
A good sales reporting system assists not only the management in exercising control but it can even help sales personnel in their self-improvement. Recording sales performance in a written form forces an individual salesperson to check their own work. They become their own critics, and self-critics is often more valuable and effective than others. This motivates sales person to improve coordination of their efforts with sales management plans and the management process functions more smoothly.
Purpose of Sales Reports
General purpose of sales report is to provide information for measuring performance. Additional purposes are
1. To provide data for evaluating sales person’s performance: these reports provide details concerning account and prospects called on, number of calls made, orders obtained, days worked, miles travelled, selling expenses etc.
2. To help the sales person plan their work: the salesperson could plan his future work with innovative ideas and measures on the basis of past sales reports.
3. To record customer’s suggestions and complaints: sales reports helps record customer’s suggestions and complaints and their reactions to new products, service policies, policies change, advertising campaigns and so forth.
4. Gathering information: sales reports helps in gathering competitive activities, new products, market test, change in promotion policy, product policy, price policy etc.
5. To report changes in local business and economic conditions.
6. To provide information requested by marketing research data on dealer’s sales inventories and competitive products.
7. To keep the mailing list updated for promotional and catalogue material.
TYPES OF SALES REPORTS
1. Progress or call report: most companies have a progress or call report system. It is prepared individually for each call and for all calls made daily or weekly. Progress report keep management informed about the salespersons activities. It provides important data to the company about calls made by salespersons in different territories. Accordingly, the company could inform and suggest the salespersons about revisits. Usually the call report contains more detailed information such as the class of customer, other brand likings of customer, etc.
2. Expense Report: Most companies prepare expense report for reimbursement and income tax purposes. From sales management point of view, the purpose of preparing expense report is to control the nature and amount of expenses made by salespersons.
3. Sales Work Plan: a sales work plan is a work plan submits by salesperson giving details about prospect to be contacted, products to be discussed, routes to be travelled etc.
4. Potential new business report: This reports informs about prospects who may become source of new business. It provides data for evaluating the extent and effectiveness of work done the salesperson.
5. Lost sales report: This provides information for evaluating salesperson abilities to keep customers and keep customer and sell against competition. Lost sales reports provide the way to needed sales training, change in customer services policies and product improvement reason for the loss of the business.
6. Report of complaint and /or adjustment: this report provides information for analyzing complaints arising from a salesman’s work, complaint by class of customer and cost of complaint adjustment. This assists management in in detecting needed product improvements and changes in merchandising and service practice policies.