Unit 5
Leasing and Hire–purchase
Q1) Write a note on consumer finance.
A1) Consumer finance refers to granting of credit by banks and financial institutions to customers for purchase of durable and luxuries items like family car, AC, laptop, mobile phones, washing machine etc. Such type of loans is provided to increase the standard of living of people of our country. It is provided to both households and business man. Such loans are repayable within 3 months to 5 years. Some of the examples providing consumer finance in India are commercial banks, Bajaj Finance Ltd., Muthoot Finance Ltd. Etc.
Various sources of consumer credit are mentioned are-
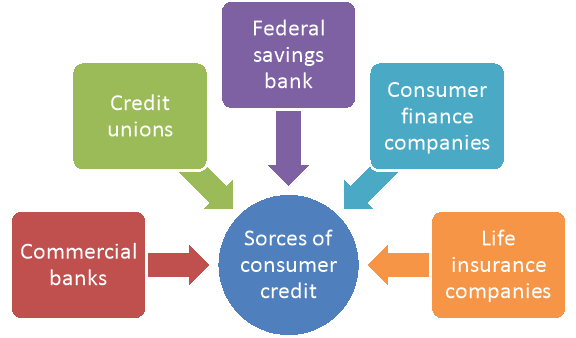
Figure: Sources of consumer credit
- Commercial banks:
• single payment loan
• personal instalment loans
• credit cards
• passbook loans
2. credit unions:
• personal instalment loans
• share-draft credit plans
• second mortgages
3. Federal savings banks:
• personal instalment loans
• home improvement loans
• education loans
• savings account loans
4. Consumer finance companies
- Personal instalment loans
- Second mortgages
5. Life insurance companies:
- Single payment or partial payment loans
Q2) State the advantages and disadvantages of consumer finance. 8
A2) The advantages of consumer finance are mentioned under the following points-
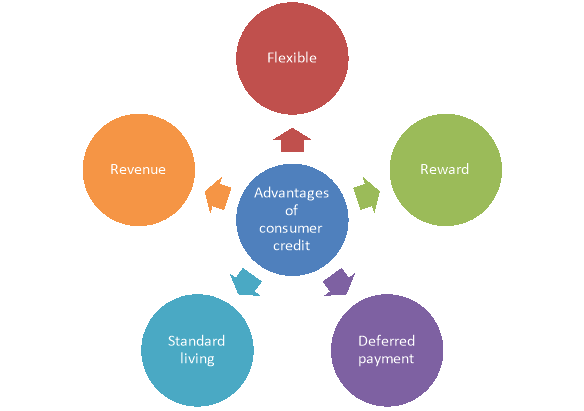
Figure: Advantages consumer credit
- It is a flexible method of credit for consumers because they access to such credits with the help of credit cards to purchase the durable and semi-durable products.
- It provides different types of rewards to the consumers like cash back, discount, coupons, gifts etc. on their credit purchases.
- It allows the consumers to make deferred payments on the purchases. Thus it enables them to purchase products which may not possible for them if payment has to be made at one time.
- It increases standard of living of people of an economy as such loans are provided to purchase luxuries goods and services.
- The banks/ financial institutions able to earn good revenue from such loans because the interest rate charged is higher as compared to other types of loans.
Some of the disadvantages of consumer finance are highlighted under the following points-
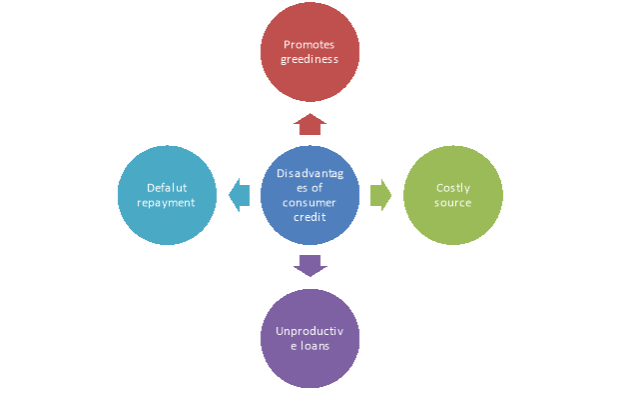
Figure: Disadvantages of consumer credit
- It promotes temptation and greediness among the borrowers because it makes credit more affordable for consumers.
- It becomes a costly source of credit for borrowers because the interest rate is high in case of consumer credit.
- It promotes unproductive loans only which unable to contribute to the GDP of an economy.
- There is the risk of default in repayment of loans.
Q3) Write a note on housing finance. 5
A3) Housing finance refers to extension of loan to consumers for construction of residential house, purchase of house, purchase of flat, repayment of housing loan etc. National Housing Bank is the apex institution in housing finance sector. The housing finance industry is composed of different hosing finance companies and customers. Some of the housing finance companies in India are-
- HDFC ltd.
- LIC Housing finance
- DFHL
- Baja Finance Ltd.
- Indiabulls Housing Finance Ltd.
- Piramal Housing Finance Ltd.
Moreover, commercial banks also provide housing finance facilities to customers. Housing finance involves the following products-
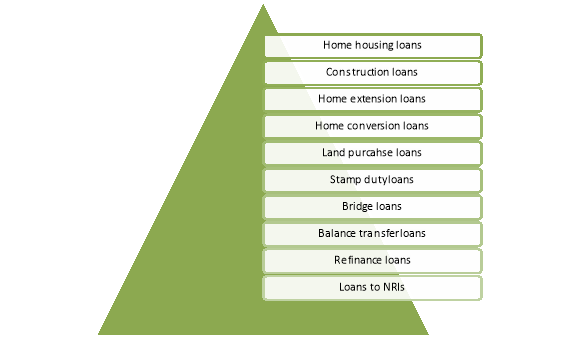
Figure: Housing loan products
- Home purchase loans
- Home construction loans
- Home extension loans
- Home conversion loans
- Land purchase loans
- Stamp duty loans
- Bridge loans
- Balance transfer loans
- Re-finance loans
- Loans to NRIs.
Q4) Discuss the housing finance policy of India. 8
A4) The Government of India formulated Housing finance policy with objectives to firstly to provide affordable housing finance system and to accommodate urban dwellers with subsidized rental programmes. Various aspects of housing finance policy are mentioned under the following heads-

Figure: Hosing finance policy
- It Improves supply of housing finance by
- Formulating public sector Institutions for promotion and execution of housing projects/programmes.
- Extending subsidy for building houses for the poor section of the society.
- Offering tax incentives to encourage promoters/builders/developers in the private sector to take up large housing projects.
2. It improves demand for houses by
- Introducing schemes to the EWS section for construction of houses.
- Promoting institutional/bank lending for housing.
- Introducing tax incentives for buying a house.
3. It improves supply of housing finance at affordable rates through
- Offering tax incentives for housing finance companies/ mortgage banks
- Creation/promotion of apex housing finance organizations to facilitate policy issues as well as facilitate refinance arrangements to the mortgage originators at affordable rates
- Permitting issue of tax free bonds by select Institutions aimed at facilitating availability of cheap funds for the housing finance sector
- Creation of an institutional framework to enable mortgage originators raise money against their home loan portfolio either through securitization or through covered bonds or permitting deposit based schemes
- Making available to Insurance /pension funds investment in securitized/ mortgage based security papers
- Introduction of pragmatic enforcement laws to enforce security in case of delinquencies
- Facilitating effective mortgage/title insurance/guarantee schemes
Q5)Write a small note on NHB. 5
A5) The National Housing Policy, 1988 envisaged the setting up of NHB as the apex level institution for housing. Accordingly, NHB was established under the NHB Act, 1987. The entire paid up capital is contributed by the RBI. It was established to fulfil the objectives, namely-
- To promote a sound, healthy, viable and cost effective housing finance system to cater to all segments of population and to integrate the housing finance system.
- To promote a network of dedicated housing finance institutions to adequately serve various regions and different income groups.
- To augment resources for the sector and channelize them for housing
- To make housing credit affordable.
- To supervise the activities of housing finance.
- To encourage public agencies to emerge as facilitators and suppliers of serviced land, for housing.
Q6) What is venture capital? State the features of venture capital. 5
A6) Venture capital is a type financing where the financing company provides equity capital to the highly risky projects related to involvement of sophisticated technology. The Venture Capital Company makes equity participation with the project and provides all technical and financial guidance for the growth of the project. Once the project started earning profit it makes disinvestment from the project. Some examples of venture capital company are-Blume Ventures, IDG Ventures, Accel Partners etc.
Features of venture capital
Some of the essential features of venture capital are-
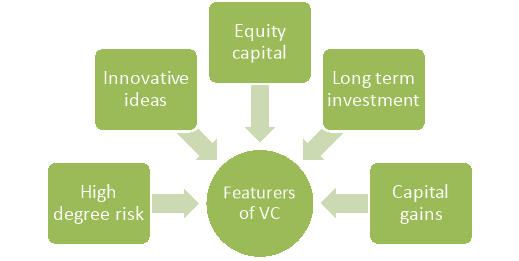
Figure: Features of venture capital
- It involves high degree of risk as it makes investment in highly risky projects.
- It provides financing facility to the projects that involves sophisticated technology and innovative ideas.
- It provides equity capital to the projects and hence participates in management of the project.
- It is a long term investment because it invests in start-up firms and continues with the project till it starts earning profit.
- It is interested in capital gains because it invests in equity capital of the projects.
Q7) Discuss the stages of venture capital financing. 5
A7) The venture capitalists supply the funds to projects in every stages of progress instead of one time investment. Different stages of venture capital financing are as follows-
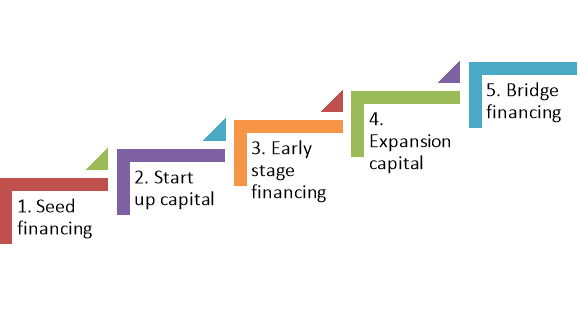
Figure: Venture capital process
- Seed financing/Early stage financing: This is the preliminary stage of venture capital financing. Funds are provided for preliminary activities like research and development, create a sample product, establish an administrative set up etc.
- Start-up capital: In this stage fund is provided to start up the project by recruiting managerial personal, additional market research, promotion of products etc.
- Early stage financing: At this stage, the project the surviving in the market by increasing its sales. The venture capitalist supply fund to increase its productivity, increase market share and increase the efficiency of management.
- Expansion capital: In this stage, the venture capitalist supply fund to expand and diversify its business, enter in the new market and grow rapidly to increase its revenue.
- Bridge financing: In this stage, the venture capitalist helps to find out a partner or acquisition opportunity or attract public financing. In this stage, the project becomes matured and hence the venture capitalist disinvests from the business.
Q8) Define factoring. Discuss the types of factoring services. 5
A8) Factoring refers to selling of trade receivables (bills of exchange and promissory note) by the owner of business firm (client) to a factor (financial intermediary) to get immediate cash to manage short term finance for his business. Under this method of financing the trade receivables are sold at a discount to the factor. It has essential characteristics of-
- It helps to manage scarcity of short term funds in the business.
- The owner of trade receivables sell it to the factor.
- It is useful both for domestic and international trade.
- It operates under money market.
Types of factoring
Depending on the nature of services provided by the factors, it is divides under the following heads-
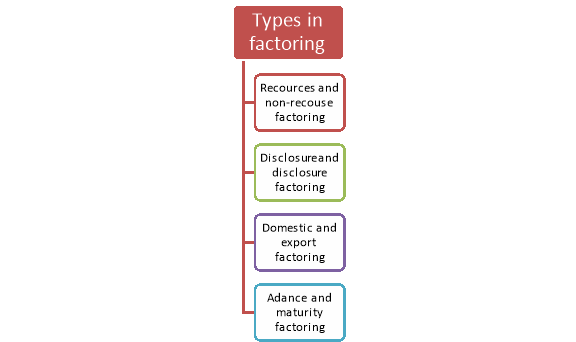
Figure: Types of factoring
- Recourse and non-recourse factoring:
Under recourse financing, the firm/client who get discounted bill from factor is not discharged from debt until and unless the factor recover the bill amount from the drawee. If the factor unable to recover the bill amount than the firm is liable to discharge the debt.
On the other hand, under non-recourse financing the firm/client is not liable for the debt to the factor if the amount of the trade bill is irrecoverable from the drawee.
2. Disclosed and undisclosed factoring:
Under disclosed factoring, the firm mentions the name of factor in the invoice/bill asking the drawee to pay the debt amount to the factor.
In case of undisclosed factoring the name of the factor is not mentioned in the invoice/trade bill. Here the factor realises the debt from the drawee/debtor in the name of the firm.
3. Domestic and export factoring:
Under domestic factoring, the parties involved in the factoring i.e, customer, client and factor are resident of the same country.
Under export factoring, the drawer and drawee both resided in different country.
4. Advance and maturity factoring:
Under advance factoring, the factor advances money to the firm/client against uncollected trade receivables.
In case of maturity factoring, the banks collects the bills amount on maturity date from the payer and credit the collected amount in the respective account of client.
Q9) State the advantages and disadvantages of factoring. 8
A9) The factoring service is beneficial for traders. Some of the significant benefits of factoring are-
- Factoring service is one of the reliable sources for the business firm to get immediate cash flow of fund by selling the invoices or trade receivables.
- Factoring facilitates the business firm to manage their working capital effectively.
- Non-recourse factoring protects the business firm from risk of bad debt because the client is discharged from liability non-payment by the payer.
- Factoring promotes trade and business in the economy by strengthening their credit capacity. It supplements the bill discounting capacity of commercial banks.
- Growth of factoring business brings price competitiveness in the market. The suppliers get immediate flow of cash and hence they able to increase their production/supply which brings competition in the market.
The factoring service also suffers from some the following disadvantages-
- The factoring is considered as source of financing because the suppliers/sellers will not get 100 per cent of the invoice/bill amount. They received 70-90 per cent of the invoice/bill amount.
- Lack of secondary market is a hurdle for factoring service. The factor cannot sell the invoices/trade bills in the secondary market which creates difficulty in smooth flow of cash in the economy.
- Sometimes the relation between the customer and company decorates because the factors are provided the responsibility to collect the invoice amount from the customer.
- Use of factoring as a source of financing leads to decline in profit margin of clients because they receive discounted amount from the factor.
- Factoring allows advances against the commercial invoice only. It excludes other sector of the economy which is a big drawback of this service.
Q10) Write a note on credit rating. 5
A10) Credit rating simply means rating of the credit worthiness of a company and assessment of the capacity of an issuer for repayment of principal and interest on debt by an independent agency. According to CRISIL, “Credit rating is an unbiased and independent opinion as to issuer’s capacity to meet its financial obligations. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy/ sell or hold a particular security”. Different credit rating agencies like CRISIL, CARE etc. provide ratings for financial institutions, banks, financial products and instruments, financial services etc. depending on which the investors make investment decision.
Features of credit rating
Some of the essential features of credit rating are mentioned below-
- It assesses the credit risk associated with a particular financial instrument, company, service etc.
- It provides rating in symbols like AAA, AA, A+, BBB etc. which implies credit repayment capacity of the company or financial instrument.
- Rating is done after considering the factors like financial and non-financial parameters, past credit etc.
- It provides guidance to investors by informing them about the credit worthiness of the interested investment avenue.
- Credit rating involves in depth study about the company depending on the information supplied by the issuer (of debt security) and also the information collected from various other sources, including personal interactions with various institutions.
Q11) State the advantages and disadvantages of credit rating. 8
A11) Some of the advantages of credit rating are highlighted in the following-
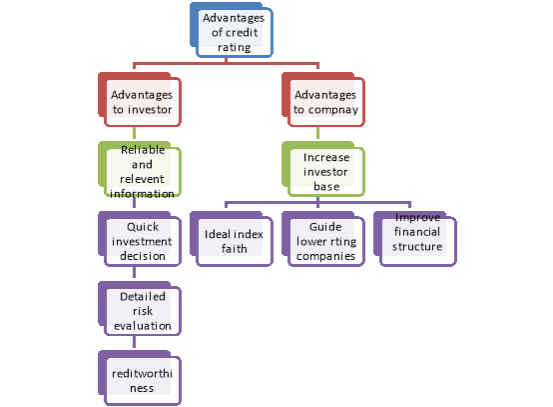
Figure: Advantages of credit rating
A. Advantages to Investors
1. It provides relevant and reliable information to investors at low cost.
2. It enables investors to take quick investment decision on the basis of ratings.
3. It helps the investors to undertake a detailed risk evaluation. It helps the investors to arrive at a meaningful and consistent conclusion regarding the relative credit quality of the security.
4. It suggests the creditworthiness of the instrument and indicates the degree of risk involved in the instrument. Hence the investors can make direct investment decisions.
B. Advantages to Issuers
1. It acts as an ideal index of faith placed by the market in the issuers.
2. It increases the investor base. This enables the rated companies to raise any amount required at lower cost without difficulty.
3. It acts as a guide to companies scoring lower rating. This enables the management to take steps on their operating and marketing risks. This will change the perception against the companies in the market.
4. It encourages discipline among corporate borrowers to improve their financial structure and performance to get better rating.
The disadvantages of credit rating are highlighted below-
- It provides only guidance to investors in determining the level of risk associated with the debt instrument but unable recommended the investors/creditors to buy/sell or hold securities.
- In most of the cases, the rating is done on the basis of the information supplied by the issuer themselves which may not reliable and valid.
- Rating is a static study of present and past data of a company ignoring some dynamic factors. This may lead to changes in the rating.
4. Different agencies provide different rating for the same instrument. In this way the investors may got confused.
5. If the staffs of credit rating agency are inexperienced or less skilled, then the rating may not be perfect.
Q12) Discuss about the regulatory measurers of credit rating. 8
A12) SEBI Regulations, 2003 require every credit rating agency to follow the code of conduct as given below:
1. A credit rating agency shall make all efforts to protect the interests of investors.
2. A credit rating agency, in the conduct of its business, shall observe high standards of integrity, dignity and fairness in the conduct of its business.
3. A credit rating agency shall fulfil its obligations in a prompt, ethical and professional manner.
4. A credit rating agency shall at all times exercise due diligence, ensure proper care and exercise independent professional judgement in order to achieve and maintain objectivity and independence in the rating process.
5. A credit rating agency shall have a reasonable and adequate basis for performing rating evaluations, with the support of appropriate and in depth rating researches. It shall also maintain records to support its decisions.
6. A credit rating agency shall have in place a rating process that reflects consistent and international rating standards.
7. A credit rating agency shall not indulge in any unfair competition nor shall it wean away the clients of any other rating agency on assurance of higher rating.
8. A credit rating agency shall keep track of all important changes relating to the client companies and shall develop efficient and responsive systems to yield timely and accurate ratings. Further a credit rating agency shall also monitor closely all relevant factors that might affect the creditworthiness of the issuers.
9. A credit rating agency shall disclose its rating methodology to clients, users and the public.
10. A credit rating agency shall not make any exaggerated statement, whether oral or written to the client either about its qualification or its capability to render certain services or its achievements with regard to the services rendered to other clients.
11. A credit rating agency shall not make any untrue statements, suppress any material fact or make any misrepresentation in any documents, reports, papers or information furnished to the Board, stock exchange or public at large.
12. A credit rating agency shall maintain an appropriate level of knowledge and competence and abide by the provisions of the Act, regulations and circulars, which may be applicable and relevant to the activities carried on by the credit rating agency. The credit rating agency shall also comply with award of the Ombudsman passed under Securities and Exchange Board of India (Ombudsman) Regulations, 2003.
13. A credit rating agency shall ensure that there is no misuse of any privileged information including prior knowledge of rating decisions or changes.
14. A credit rating agency or any of his employees shall not render, directly or indirectly any investment advice about any security in the publicity accessible media.
15. A credit rating agency shall maintain an arm’s length relationship between its credit rating activity and any other activity.
Q13) Write a note on CRISIL. 5
A13) The credit rating agencies operating in India are discussed below
- Credit Rating Information Services of India Ltd. (CRISIL)
CRISIL is the first credit rating agency in India. It is a public limited company established in 1987 in the private sector. It is promoted jointly by ICICI and UTI. It started its operations on 1st January 1988. Its objectives is to accord credit rating to public limited companies which desire to float share capital, debentures, public deposits or commercial paper to raise finance from the public.
Objectives of CRISIL
1. To assist the investors in making investment decisions in fixed interest securities.
2. To guide the investors in understanding the risk associated with a particular debt instrument.
3. To help the companies raise large funds at a lower cost.
4. To create awareness of the concept of credit rating amongst corporations, merchant bankers, brokers, regulatory bodies.
5. To provide regulators with a market driven system in order to ensure discipline and a healthy growth of capital markets.
The services rendered by CRISIL may be summarised as below:
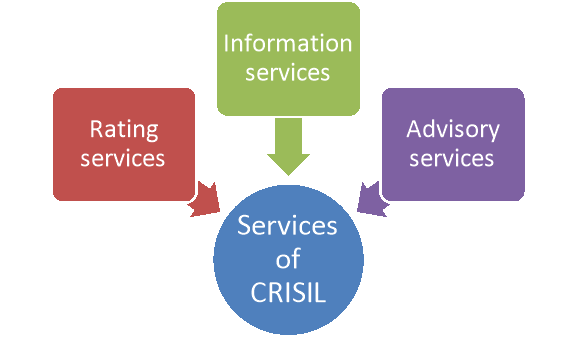
Figure: Services of CRISIL
- Rating services: The main business of CRISIL is rating debentures, deposits, preference shares as well as commercial paper. Rating services is also provided to chit funds, real estate developers, banks etc.
- Information services: CRISIL offers information services also. Its main product ‘CRISIL CARD’ provides corporate and balance sheet data for the sake of analysis. It assesses the outlook and solvency of the concerned companies on the basis of published data. CRISIL 500 Equity Index is an index newly launched on the basis of 500 companies representing 74% of market capitalization of the Mumbai Stock Exchange.
- Advisory services: It also offers services to the Governments, banks, financial institutions etc. It provides advisory services in the areas of energy, transport, urban infrastructure, tourism, economy, corporate, capital markets, and financial services. It also undertakes credit and counter party ratings for corporates.