CO
UNIT-4Input/Output Organization Q1) Explain different types of Cables used in computersA1) With so many types of cables, it’s hard to find a singular source of information that highlights the important differences between them all. Here’s an overview of the most common computer cable types you’ll encounter when dealing with computers.1. VGA CableAlso known as D-sub cable, analogue video cable
Connect one end to: computer monitor, television (PC input port)Connect other end to: VGA port on computer (see image below)
2. DVI Cable
Connect one end to: computer monitorConnect other end to: DVI port on computer (see image below)
However, there are 2 types of DVI, DVI-I and DVI-D.
DVI-D does not have the extra pins around the long pin, this is also a pure digital signal over DVI-I.3. HDMI Cable
Connect one end to: computer monitor, televisionConnect other end to: HDMI port on computer (see image below)Note: If you're hooking up a television to your computer, then we would recommend that you use a HDMI cable as your PC cable connection since it is able to transmit both display and sound - So you can not only use your TV screen as a monitor, but also make use of your TV speakers to play PC audio.
4. PS/2 Cable
Connect one end to: PS/2 keyboard, PS/2 mouseConnect other end to: PS/2 ports on computer (see image below)Purple PS/2 port: keyboard Green PS/2 port: mouse
5. Ethernet CableAlso known as RJ-45 cable
Connect one end to: router, network switchConnect other end to: Ethernet port on computer (see image below)
6. 3.5mm Audio CableAlso known as phone connector (since 3.5mm jacks are often found on mobile phones too)
Connect one end to: computer speakers, 3.5mm headphones, 3.5mm microphoneConnect other end to: audio ports on computer (see image below use Green socket)Green audio port: computer speakers or headphones Pink audio port: microphone Blue audio port: MP3 player, CD player, DVD player, turntable, electric guitar etc (line-in port to play and record sounds from the above devices)
7. USB CableFor USB computer cable connections, there are two popular formats: USB 2.0 and the newer USB 3.0How to tell USB 2.0 and 3.0 cables apart: USB 3.0 cables have a blue tip, and sometimes you can find a SS "Super Speed" label on it.
Since USB was intended to be the one computer cable connection to replace them all, it's no surprise that the possible uses for a USB port are quite mind-blowing. For this computer cable guide, we have listed its more common uses below:Connect one end to: USB deviceStorage devices: USB flash drive, external hard drive, external optical drive Input devices: USB keyboard (wired and wireless), USB mouse (wired and wireless), webcam, scanner, gamepad Output devices: printer, all-in-one office machine, USB speaker Wireless adapters: network (Wi-Fi) adapter, Bluetooth adapter, 3G adapter Data (and charging) cable for mobile devices such as mobile phone, tablet, MP3 player Connect other end to: USB ports on computer (see image below)How to tell USB 2.0 and 3.0 ports apart: USB 2.0 ports have black tips while USB 3.0 ports come with blue tips. See image below:
USB 3.0 is backwards-compatible... meaning that you can connect a USB 2.0 device to a USB 3.0 port and vice versa (but the USB 3.0 devices hooked up to a USB 2.0 port will perform at lowered rates)There are also USB cables which connect new external backup drives (see below), these are described as USB-A to Micro-B
8. Computer Power Cord (Kettle Plug)
Connect one end to: AC power socketConnect other end to: power supply unit (see image below), computer monitorNote: Always turn off your power supply unit (with the 1-0 switch at the back) before connecting a power cord to it.
9. Thunderbolt/USB-CMostly seen on laptops and Apple Macs these cables are high speed and are capable of carrying Data, video and other information.There are 2 current types of Thunderbolt, the older version Thunderbolt 2 is seen below but this can also be confused with Mini Display ports as they look identical and only visual difference is the picture beside the port. Thunderbolt 2 (left) has a lightning symbol and carries Data and video.The Mini Display Port (right) will only carry Video.
And Thunderbolt 3 also had known as USB-C on Apple Macs.
10. Display Port
Display Port is the best to use if you require a fast, high-resolution image.
The cable has better quality over HDMI and is the best option if you have this interface.
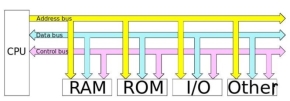
Q2) Explain Buses in computer peripheralsA2) Inside computers, there are many internal components. In order for these components to communicate with each other, they make use of wires that are known as a ‘bus’.A bus is a common pathway through which information flows from one computer component to another. This pathway is used for communication purpose and it is established between two or more computer components. We are going to check different computer bus architectures that are found in computers.Different Types of Computer Buses
The Computer BusesFunctions of Buses in ComputersSummary of functions of buses in computers1. Data sharing - All types of buses found in a computer transfer data between the computer peripherals connected to it.The buses transfer or send data either in the serial or parallel method of data transfer. This allows for the exchange of 1, 2, 4 or even 8 bytes of data at a time. (A byte is a group of 8 bits). Buses are classified depending on how many bits they can move at the same time, which means that we have 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit or even 64-bit buses.2. Addressing - A bus has address lines, which match those of the processor. This allows data to be sent to or from specific memory locations.3. Power - A bus supplies power to various peripherals connected to it.4. Timing - The bus provides a system clock signal to synchronize the peripherals attached to it with the rest of the system.The expansion bus facilitates easy connection of more or additional components and devices on a computer such as a TV card or sound card.Bus TerminologiesComputers have two major types of buses:1. System bus: This is the bus that connects the CPU to the main memory on the motherboard. The system bus is also called the front-side bus, memory bus, local bus, or host bus.2. A number of I/O Buses, (I/O is an acronym for input/output), connecting various peripheral devices to the CPU. These devices connect to the system bus via a ‘bridge’ implemented in the processors' chipset. Other names for the I/O bus include “expansion bus", "external bus” or “host bus”.Expansion Bus TypesThese are some of the common expansion bus types that have ever been used in computers:ISA - Industry Standard Architecture EISA - Extended Industry Standard Architecture MCA - Micro Channel Architecture VESA - Video Electronics Standards Association PCI - Peripheral Component Interconnect PCI Express (PCI-X) PCMCIA - Personal Computer Memory Card Industry Association (Also called PC bus) AGP - Accelerated Graphics Port SCSI - Small Computer Systems Interface. The 8 Bit and 16 Bit ISA Buses
8 Bit and 16 Bit ISA BusesISA BusThis is the most common type of early expansion bus, which was designed for use in the original IBM PC. The IBM PC-XT used an 8-bit bus design. This means that the data transfers take place in 8-bit chunks (i.e. one byte at a time) across the bus. The ISA bus ran at a clock speed of 4.77 MHz.For the 80286-based IBM PC-AT, an improved bus design, which could transfer 16-bits of data at a time, was announced. The 16-bit version of the ISA bus is sometimes known as the AT bus. (AT-Advanced Technology)The improved AT bus also provided a total of 24 address lines, which allowed 16MB of memory to be addressed. The AT bus was backward compatible with its 8-bit predecessor and allowed 8-bit cards to be used in 16-bit expansion slots.When it first appeared the 8-bit ISA bus ran at a speed of 4.77MHZ – the same speed as the processor. Improvements done over the years eventually made the AT bus ran at a clock speed of 8MHz.Comparison Between 8- and 16-Bit ISA Bus
MCA (Micro Channel Architecture)IBM developed this bus as a replacement for ISA when they designed the PS/2 PC launched in 1987.The bus offered a number of technical improvements over the ISA bus. For instance, the MCA ran at a faster speed of 10MHz and supported either 16-bit or 32-bit data. It also supported bus mastering - a technology that placed a mini-processor on each expansion card. These mini-processors controlled much of the data transfer allowing the CPU to do other tasks.One advantage of MCA was that the plug-in cards were software configurable; this means that they required minimal intervention by the user when configuring.The MCA expansion bus did not support ISA cards and IBM decided to charge other manufacturers royalties for use of the technology. This made it unpopular and it is now obsolete technology.The EISA Bus
The EISA Bus Slots (on the left) Where EISA Cards Were ConnectedEISA (Extended Industry Standard Architecture)This is a bus technology developed by a group of manufactures as an alternative to MCA. The bus architecture was designed to use a 32-bit data path and provided 32 address lines giving access to 4GB of memory.Like the MCA, EISA offered a disk-based setup for the cards, but it still ran at 8MHz in order for it to be compatible with ISA.The EISA expansion slots are twice as deep as an ISA slot. If an ISA card is placed in an EISA slot it will use only the top row of connectors, however, a full EISA card uses both rows. It offered bus mastering.EISA cards were relatively expensive and were normally found on high-end workstations and network servers.VESA BusIt was also known as the Local bus or the VESA-Local bus. VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association) was invented to help standardize PCs video specifications, thus solving the problem of proprietary technology where different manufacturers were attempting to develop their own buses.The VL Bus provided 32-bit data path and ran at 25 or 33 MHZ. It ran at the same clock frequency as the host CPU. But this became a problem as processor speeds increased because, the faster the peripherals are required to run, the more expensive they are to manufacture.It was difficult to implement the VL-Bus on newer chips such as the 486s and the new Pentiums and so eventually the VL-Bus was superseded by PCI.
VESA slots had an extra set of connectors and thus the cards were larger. The VESA design was backward compatible with the older ISA cards.
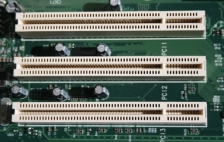
Features of the VESA local bus card:32-bit interface 62/36-pin connector 90+20 pin VESA local bus extension Peripheral Component InterconnectPeripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is one of the latest developments in bus architecture and is the current standard for PC expansion cards. Intel developed and launched it as the expansion bus for the Pentium processor in 1993. It is a local bus like VESA, that is, it connects the CPU, memory, and peripherals to a wider, faster data pathway.PCI supports both 32-bit and 64-bit data width; it is compatible with 486s and Pentiums. The bus data width is equal to the processor, such as a 32-bit processor would have a 32-bit PCI bus, and operates at 33MHz.PCI was used in developing Plug and Play (PnP) and all PCI cards support PnP. This means a user can plug a new card into the computer, power it on and it will “self-identify” and “self-specify” and start working without manual configuration using jumpers.Unlike VESA, PCI supports bus mastering that is, the bus has some processing capability and thus the CPU spends less time processing data. Most PCI cards are designed for 5v, but there are also 3v and dual-voltage cards. Keying slots used help to differentiate 3v and 5v cards and also to make sure that a 3v card is not slotted into a 5v socket and vice versa.The PCI Slots
Accelerated Graphics PortThe need for high quality and very fast performance of video on computers led to the development of the Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP). The AGP Port connects to the CPU and operates at the speed of the processor bus. This means that video information is sent more quickly to the card for processing.The AGP uses the main PC memory to hold 3D images. In effect, this gives the AGP video card an unlimited amount of video memory. To speed up the data transfer, Intel designed the port as a direct path to the PC’s main memory.Data transfer rate ranges from 264 Mbps to 528mbps, 800 Mbps up to 1.5 Gbps. AGP connector is identified by its brown colour.Personal Computer Memory Card Industry Association (PC Card)The Personal Computer Memory Card Industry Association was founded to give a standard bus for laptop computers. So, it is basically used in the small computers.Small Computer System InterfaceShort for Small Computer System Interface, a parallel interface standard used by Apple Macintosh computers, PCs and Unix systems for attaching peripheral devices to a computer.The SCSI Port
Universal Serial Bus (USB)This is an external bus standard that supports data transfer rates of 12 Mbps. A single USB port connects up to 127 peripheral devices, such as mice, modems, and keyboards. The USB also supports hot plugging or insertion (ability to connect a device without turning the PC off) and plug and play (You connect a device and start using it without configuration).We have two versions of USB:USB 1xFirst released in 1996, the original USB 1.0 standard offered data rates of 1.5 Mbps. The USB 1.1 standard followed with two data rates: 12 Mbps for devices such as disk drives that need high-speed throughput and 1.5 Mbps for devices such as joysticks that need much less bandwidth.USB 2xIn 2002 a newer specification USB 2.0, also called Hi-Speed USB 2.0, was introduced. It increased the data transfer rate for PC to a USB device to 480 Mbps, which is 40 times faster than the USB 1.1 specification. With the increased bandwidth, high throughput peripherals such as digital cameras, CD burners, and video equipment could now be connected with USB.IEEE 1394The IEEE 1394 is a very fast external serial bus interface standard that supports data transfer rates of up to 400Mbps (in 1394a) and 800Mbps (in 1394b). This makes it ideal for devices that need to transfer high levels of data in real-time, such as video devices. It was developed by Apple with the name firewire.A single 1394 port can connect up 63 external devices.It supports Plug and play Supports hot plugging, and Provides power to peripheral devices. The IEEE 1394 Expansion Card
Q3) Explain Device driversA3) Device Driver in computing refers to a special kind of software program or a specific type of software application which controls a specific hardware device that enables different hardware devices for communication with the computer’s Operating System
A device driver communicates with the computer hardware by computer subsystem or computer bus connected to the hardware. Device Drivers are very essential for a computer system to work properly because without device driver the particular hardware fails to work accordingly means it fails in doing a particular function/action for which it has been created.In a very common way, most term it as only a Driver also when someone says Hardware Driver that also refers to this Device Driver.
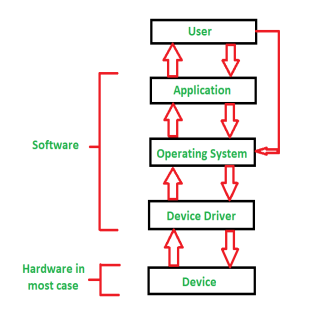
Working of Device Driver: Device Drivers depend upon the Operating System’s instruction to access the device and performing any particular action. After the action they also shows their reactions by delivering output or status/message from hardware device to the Operating system. For Example a printer driver tells the printer in which format to print after getting instruction from OS, similarly A sound card driver is there due to which 1’s and 0’s data of MP3 file is converted to audio signals and you enjoy the music. Card reader, controller, modem, network card, sound card, printer, video card, USB devices, RAM, Speakers etc need Device Drivers to operate.The following figure illustrates the interaction between user, OS, Device driver and the devices:
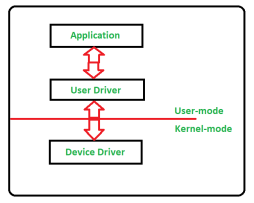
Types of Device Driver:For almost every device associated with the computer system there exist Device Driver for the particular hardware. But it can be broadly classified into two types i.e.,Kernel-mode Device Driver – This Kernel-mode device driver includes some generic hardware which loads with operating System as part the OS these are BIOS, motherboard, processor and some other hardware which are part of kernel software. These includes the minimum system requirement device drivers for each operating system. 2. User-mode Device Driver –Other than the devices which are brought by kernel for working of the system the user also bring some devices for use during the using of a system that devices needs device drivers to functions those drivers falls under User mode device driver. For example, user needs any plug and play action that comes under this. Virtual Device Driver: There are also virtual device drivers (VxD), which manages the virtual device. Sometimes we use same hardware virtually at that time virtual driver controls/manages the data flow from different application used by different users to the same hardware.It is essential for a computer to have the required device drivers for all its parts to keep the system running efficiently. Many device drivers are provided by manufactures from beginning and also, we can later include any required device driver for our system.4. Explain Input devices
The device which are connected to computer and they are used to send the data to the computer internally, are known as the input devices. Following are some important input devices;Mouse: Mouse is the one of the most common devices that one would find in a desktop. It is normally plugged with the USB connection. It would be connected through the PS/2 port which is located on the back of the computer. In older system, one might find the serial port which was used to move the move around. The old mouse contained ball inside of it which helped it move. But nor the trend has changed the mouse that one uses contains some LED light. They are called the laser mouse. The LED light now emits out of the mouse sensing that where the mouse is being moved. The installation of mouse is easy, one can just plug the mouse and the drivers would be searched by windows itself. The mouse can be configured from the control panel where the speed of it can be improved.Keyboard: it is the famous device that is being used today and it is connected through a USB connection at the back of the computer. Old keyboards used to have the Mini DIN PS/2 connection with them; one would have to go through the manufacturer's website to know that what are the drivers for the keyboard and then can get them installed when he connects the keyboard with the computer.Touch screen: Touch screen is becoming common as well. They are normally used on the mobile phones and other smart devices. Also, the tablets also contain this feature. Now it is even common to find a computer's large screen which works with the touch screen system. It makes it very easy to type and navigate and one can bring the keyboard on the screen and type it there as well hence one doesn't have to install the keyboard. The configurations and the installation of the touch screen are also done in a display when it is bought.Scanner: At a time, the fax machines were widely used by the people and till now, they use it. But now the tables have turned and people tend to use the scanners. The scanners have the ability to turn the paper's image into a digital one hence sending the data from one place to another while keeping the same paper with us is now an easy task and the data can be sent more easily through the internet. The scanners are now used a lot and one can simply scan a paper and save it in any format he wants to.Barcode reader: If one goes to some super market or the retail environment, one would see the barcode. It's a machine that is used to read the code which is printed at the back of the products. The connection of the bar code is normally made through the USB connection. Some old versions of the bar codes also use the PS.2 connections to get connected to the computer. The barcodes use the laser technology to read the barcode. The light comes and goes when the code is exposed to the barcode reader. This eye can directly damage one's eye as well so one has to be careful while using this machine. The barcode contains a specific driver when it is connected, the driver is detected by the windows and hence it can work properly.KVM: If one is working in an environment where there is a single display but there are many different computers connected to it, the one is using the KVM. KVM means the keyboard, video and the mouse. Here if one wants to move to another device, he just has to push a single button to get to other device. This set can be centralized and the KVM can be used to switch between all the computing devices.Microphone: the putting of voice in our computer is very common. It is done by the chat or it is even done for the voice reorganization software's which are available in the market. Microphones on not only at the headset, but they can be found separately and are there in the laptops as well. They also have the specific drivers and the configuration can be made through the control panel.Biometric devices: these devices are used as the security tools. They are mostly used on some portable devices which tend to go away from one. If one tries to use the laptop, he might find there is a finger print reader there and hence it is protected since only the administrator who has set it up can log in to the computer.Game pads: Game pad is the wonderful thing for the gamers. It allows the gamers to have some control over the gaming experience.Joysticks: it is the gaming input which is widely used. It is a stick which has many buttons on it.Digitizer: the digitalizing pad has some specialized pins that allow the user to draw on it very carefully and accurately. They are for those who have got some artistic abilities and they are installed with the driver.Q5) Explain Multimedia devices:A5) Multimedia devices have become so common these days and now they are an important part of our lives. Following are a few devices which are as follows;Digital cameras: the digital cameras are the standalone cameras which are used by the individuals. These days almost everyone has got a digital camera and they are even embedded into the mobile phone where they can be used to take picture. The digital cameras when connected to the PC for transfer of pictures require the driver to get installed and that driver comes with the accessories.Microphone: if one wants to do some conferences or the voice chat, he would be meeting the microphone. They are available as the separated ones as well which can be easily used. They are normally connected through some USB connection and there is the digital connector which is associated with it to provide the high quality.Webcam: Having a video is now a great need of the everyday life. Now it is very common to find some built in cameras into the displays which are being used these days. Specially, they are so common in the laptop and if they are not present, it is pretty common to get it connected and it is done pretty cheap amount. One can also enjoy the live video if it is plugged through the 802.11 wireless connections which go into the USB connection in the computer.Camcorder: Most of the video conference has to be recoded and hence one needs the camcorders. They are normally done for some live videos. Normally those people, who upload videos on the video sharing websites like YouTube etc., use this tool to record the videos and then can upload them on the PC, were after editing, they can upload it on the website. They are not only into the digital cameras but they can be found easily on every laptop and almost every mobile phone so one can record anything anytime without any hustle. The video is stored in the flash memory. There is mostly having the large storage capacities in the digital cameras so that the videos can be recorded no matter how big they are. For transferring the videos off the camera, one would need a Firewire, it is a kind of direct HDMI connection and it can be used to display the video immediately on some display.MIDI enabled devices: MIDI stands for the Musical Instrument Digital Interface. It is actually a device which is musical one and can digitalize all of the information and can transfer it to the computer in some really standard way. Many of the application which contains these capabilities of the music use this midi as the standard format so that the information can be getting in and out of the computer. It is common to get these devices plugged into the computers with the help of some Ethernet cables and even the USB cables. While on the different side there in instrument is coated, the large din connections are used to get connected between the commuter and the device.Q6) Explain Output devices:
A6) Output devices are those devices which do not send the data into the computer, in fact through these devices, the computer communicates with the user. They contain the devices like displays, printers etc. Since they are very vital part of the computer system, so one should have enough knowledge about them. Some of these output devices are as follows;Printers: if one has the data in the computer, it is obvious that he has to take it out of the computer. There are several ways for it and one of them is the painters. These printers are available not only in the office environment and in some retail environment, but at the homes as well. One might need the printer to take out the prints of the important information he finds on the internet or the assignment which he creates. At office, many important documents are sent and received in the digitalized format and they have to be converted to the hard copy so they can be read easily. At the shops, one might find the painters which are used for printing out the receipts which are handed over to the customers. Hence printers are used in every aspect of the busy life. Printers have various types and the laser printers are the most famous type since they print really good. For printers there is much software and one must install the appropriate drivers to get them work. The configuration of the pinner can be done manually once it is connected to the computer.Speakers: many of the features which are used by us are mainly related to the audio. Doesn't matter whether one listens to the podcasts or plays music, He would need the audio to be heard. Even while watching the movie or some educational video, hearing the voice is really important part and for that purpose, one needs the speakers. The laptop contains the right left speakers which are located at these both sides. There is also a subwoofer which can be used for the mixing of the voice. Also, one can have some advanced computer speaker which can be plugged into the computer externally for the sake of better quality of the sound. The laptops have various options which ate provided to user so that he can hear the sound with different options.Display devices: one of the most integral parts of the PC is the display devices which are used. The human beings need to see that what's going on the operating system and to get in touch with the interface, they must have some display device which can show them the appropriate amount of data. Normally the display devices re pretty thin and one has many options for the display devices and they vary in prices range as well. These devices can be both non touchable and the touchscreen. These display devices are not just connected to the computers; instead, they are connected to the mobile phones as well. Also, the Tablets contain some display devices as well. These displays show us what is exactly going on there and how we can control the computer.Hence, the computer is made up of many parts and each part plays some really vital role so one should know all the parts of the computer so that he can get the knowledge about how they work, how they are installed and how they can be configured once they are connected to the computer/laptops. Q7) What is a Plug-and-play device?A7) Plug and play also referred as PnP, is an attractive phrase used for devices that work or recognized instantly whenever they are connected to computer. The major advantage of PnP device is that a user does not have to install the drivers manually and moreover the computer will itself take care of the device without manual intervention. When the device is connected it is automatically detected or recognized by the computer, new drivers will be loaded for the hardware instantly for the first-time use. Consider for example that you connect a plug and play device to one of the USB port of your computer; thus, you may notice that as soon as you connect the device it will become available within few seconds after plug-in. Besides this when you compare the plug-and-play device with non-plug-and-play device, you may notice that the device will take a very lengthy procedure for setting up the device on your computer. Perhaps in Windows based computer a plug-and-play device was first introduced in Windows 95 and retained the same for all its later versions. The role of plug-and-play devices in growing in demand nowadays as every user wants some kind of comfortability to easily access the device. Example of some plug-and-play devices are USB devices, internal or external hard disks, video cards, monitor and many other. At times there are situations where system cannot configure and load a PnP device, thus in this kind of situation you can make use of device manger, DOS drivers loaded with CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT configuration files and finally by using both DOS and operating system. But even after performing above mentioned configuration methods the devices may not be configured due to some complex operating system environment or due to some uncertainties with the computer. At times a plug-and-play device like USB device will end up in software or hardware conflict due to which it may fail to work; this failure may result in device corruption leading to data loss. Thus if you have come across any such scenario then you can make use of Remo Recover (Windows / Mac) application which can easily perform data recovery after USB flash drive not recognized by your Windows or Mac operating system. Q8) Explain Expansion slotsA8) Expansion slots are specific slots on a PC motherboard that facilitate the placement of expansion cards. They are located at the back of the computer; they allow more ports to be add to the computer. Example USB 2.0/USB 3.0, HDMIThere are many different types of motherboard expansion slots, but they all have one thing in common: They allow you to plug expansion cards into your computer and increase its functionality. While motherboards often come with on-board sound, wired networking, and video, plugging in a dedicated expansion card will result in this card being used instead of the motherboard’s built-in hardware and can increase your computer’s gaming, video playback, or sound performance. Expansion cards can also provide new functionality, such as allowing your computer to capture TV signals or access a wireless network.PCI ExpressPCI Express Motherboard Expansion Slot PCI Express (or PCIe) is the newest standard for expansion cards on personal computers. PCI Express is meant to replace older standards like PCI and AGP, mentioned below. PCIe provides significantly more bandwidth, allowing for higher performance video cards and network cards. Video cards in particular are the most common consumer use of these slots, since they need high bandwidth for maximum 3D gaming and graphics performance. PCI Express slots have different versions and numbers of lanes.PCI
PCI Motherboard Expansion Slots PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) is not to be confused with PCI Express, which is meant to replace it. Unlike PCI Express, PCI is an older standard which provides less bandwidth for expansion cards. In spite of the fact that the standard was created in 1993, new motherboards still ship with PCI slots for compatibility purposes.AGP
AGP Motherboard Expansion Slot the AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) expansion slot standard was introduced when video cards needed more bandwidth for performance than was provided by PCI. As suggested by the title, AGP slots are used for video cards. However, AGP has been largely phased out in favour of the PCI Express expansion slot standard. Unlike AGP, PCI Express provides higher bandwidth for other types of expansion cards that could use it, such as some newer, high-performance sound and network cards.ExpressCard & PC Card (or PCMCIA)PCMCIA Motherboard Expansion Slot These standards are designed to be used with portable computers such as laptops. ExpressCard is the successor to PC Card (also known as PCMCIA), and, like PCIe over PCI, has more bandwidth. Unlike PCI, these types of cards are hot-pluggable (which means you can plug them in while your laptop is running, without shutting it down first).ISA
ISA Motherboard Expansion Slot ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) is another type of expansion slot you may have heard of. It was the predecessor to PCI and you’ll only find it on much older computers. Q9) Explain System softwareA9) Software is a part of computer system that contains data or set of instructions. It is considered as set of programs, which is then executed to perform a well-defined function. A program consists of a set of instructions which are used to perform a specific task in an orderly manner.There are two types of software −System Software Application Software System SoftwareThe system software is a group of programs designed to operate, control, perform and extend the processing capabilities of the computer itself. System software is generally prepared by the computer manufacturers. These software products contain mainly programs which are written in low-level languages, understandable language where they interact with the hardware at a very basic level. It is very cumbersome to write a program in the machine language. System software acts as the interface between the hardware and the end users.Some examples of system software are Operating System, Compilers, Interpreter, Assemblers, etc.
Here is a list of some of the most prominent features of a system software −Close to the system Very fast in speed Complicated to design Difficult to understand Less interactive Smaller in size Difficult to manipulate Generally written in low-level language i.e machine language Application SoftwareApplication software products are specially designed to satisfy the needs of the user to perform the functions properly. All software applications prepared in the computer lab can come under the category of Application software.Application software may consist of a single program, such as Microsoft's notepad. It is used to write and edit a simple text. It may also consist of a series of programs, often called a software package, which work together to perform a specific task, such as a spreadsheet package.Examples of Application software are the following −Payroll Software Student Record Software Inventory Management Software Income Tax Software Railways Reservation Software Microsoft Office Suite Software Microsoft Word Microsoft Excel Microsoft PowerPoint
Features of application software are as follows −Close to the user Easy to design More interactive Slow in speed Generally written in high-level language Easy to understand Easy to manipulate and use Bigger in size and requires large storage capacity. Q10) Explain Program Language TranslatorsA10) A translator is a programming language processor that converts a computer program from one language to another. It takes a program written in source code and converts it into machine code. It discovers and identifies the error during translation.Purpose of TranslatorIt translates high-level language program into a machine language program that the central processing unit (CPU) can understand. It also detects errors in the program.Different Types of TranslatorsThere are 3 different types of translators as follows:CompilerA compiler is a translator used to convert high-level programming language to low-level programming language. It converts the whole program in one session and reports errors detected after the conversion. Compiler takes time to do its work as it translates high-level code to lower-level code all at once and then saves it to memory. A compiler is processor-dependent and platform-dependent. But it has been addressed by a special compiler, a cross-compiler and a source-to-source compiler. Before choosing a compiler, user has to identify first the Instruction Set Architecture (ISA), the operating system (OS) and the programming language that will be used to ensure that it will be compatible.InterpreterJust like a compiler, is a translator used to convert high-level programming language to low-level programming language. It converts the program one at a time and reports errors detected at once, while doing the conversion. With this, it is easier to detect errors than in a compiler. An interpreter is faster than a compiler as it immediately executes the code upon reading the code.
It is often used as a debugging tool for software development as it can execute a single line of code at a time. An interpreter is also more portable than a compiler as it is not processor-dependent, you can work between hardware architectures.AssemblerAn assembler is is a translator used to translate assembly language to machine language. It is like a compiler for the assembly language but interactive like an interpreter. Assembly language is difficult to understand as it is a low-level programming language. An assembler translates a low-level language, an assembly language to an even lower-level language, which is the machine code. The machine code can be directly understood by the CPU.Examples of TranslatorsHere are some examples of translators per type:
Advantages and Disadvantages of TranslatorsHere are some advantages of the Compiler:The whole program is validated so there are no system errors. The executable file is enhanced by the compiler, so it runs faster. User do not have to run the program on the same machine it was created. Here are some disadvantages of the Compiler:It is slow to execute as you have to finish the whole program. It is not easy to debug as errors are shown at the end of the execution. Hardware specific, it works on specific machine language and architecture. Here are some advantages of the Interpreter:You discover errors before you complete the program, so you learn from your mistakes. Program can be run before it is completed so you get partial results immediately. You can work on small parts of the program and link them later into a whole program. Here are some disadvantages of the Interpreter:There’s a possibility of syntax errors on unverified scripts. Program is not enhanced and may encounter data errors. It may be slow because of the interpretation in every execution. Here are some advantages of the Assembler:The symbolic programming is easier to understand thus time-saving for the programmer. It is easier to fix errors and alter program instructions. Efficiency in execution just like machine level language. Here are some disadvantages of the Assembler:It is machine dependent, cannot be used in other architecture. A small change in design can invalidate the whole program. It is difficult to maintain.
|
|
|
|
However, there are 2 types of DVI, DVI-I and DVI-D.
DVI-D does not have the extra pins around the long pin, this is also a pure digital signal over DVI-I.3. HDMI Cable
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The cable has better quality over HDMI and is the best option if you have this interface.
|
|
|
8-Bit ISA card (XT-Bus) | 16-Bit ISA (AT –Bus card) |
8-bit data interface | 16-bit data interface |
4.77 MHZ bus | 8-MHZ bus |
62-pin connector | 62-pin connector |
| 36-pin AT extension connection |
|
VESA slots had an extra set of connectors and thus the cards were larger. The VESA design was backward compatible with the older ISA cards.
Features of the VESA local bus card:
|
|
|
A device driver communicates with the computer hardware by computer subsystem or computer bus connected to the hardware. Device Drivers are very essential for a computer system to work properly because without device driver the particular hardware fails to work accordingly means it fails in doing a particular function/action for which it has been created.In a very common way, most term it as only a Driver also when someone says Hardware Driver that also refers to this Device Driver.
|
|
|
|
PCI Motherboard Expansion Slots PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) is not to be confused with PCI Express, which is meant to replace it. Unlike PCI Express, PCI is an older standard which provides less bandwidth for expansion cards. In spite of the fact that the standard was created in 1993, new motherboards still ship with PCI slots for compatibility purposes.AGP
AGP Motherboard Expansion Slot the AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) expansion slot standard was introduced when video cards needed more bandwidth for performance than was provided by PCI. As suggested by the title, AGP slots are used for video cards. However, AGP has been largely phased out in favour of the PCI Express expansion slot standard. Unlike AGP, PCI Express provides higher bandwidth for other types of expansion cards that could use it, such as some newer, high-performance sound and network cards.ExpressCard & PC Card (or PCMCIA)PCMCIA Motherboard Expansion Slot These standards are designed to be used with portable computers such as laptops. ExpressCard is the successor to PC Card (also known as PCMCIA), and, like PCIe over PCI, has more bandwidth. Unlike PCI, these types of cards are hot-pluggable (which means you can plug them in while your laptop is running, without shutting it down first).ISA
ISA Motherboard Expansion Slot ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) is another type of expansion slot you may have heard of. It was the predecessor to PCI and you’ll only find it on much older computers. Q9) Explain System softwareA9) Software is a part of computer system that contains data or set of instructions. It is considered as set of programs, which is then executed to perform a well-defined function. A program consists of a set of instructions which are used to perform a specific task in an orderly manner.There are two types of software −
|
|
It is often used as a debugging tool for software development as it can execute a single line of code at a time. An interpreter is also more portable than a compiler as it is not processor-dependent, you can work between hardware architectures.AssemblerAn assembler is is a translator used to translate assembly language to machine language. It is like a compiler for the assembly language but interactive like an interpreter. Assembly language is difficult to understand as it is a low-level programming language. An assembler translates a low-level language, an assembly language to an even lower-level language, which is the machine code. The machine code can be directly understood by the CPU.Examples of TranslatorsHere are some examples of translators per type:
Translator | Examples |
Compiler | Microsoft Visual Studio |
Interpreter | OCaml |
Assembler | Fortran Assembly Program (FAP) |
0 matching results found