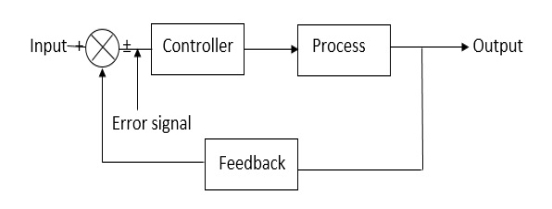
A1)
Open Loop System | Closed Loop system |
1.It does Not have any feedback. | 1. This system comprise of feedback |
2.As no feedback so easier to build. | 2.As it has feedback so difficult to build |
3.Theaccuracy of this system depends on the calibration of input. | 3.They are accuracy because of the feedback. |
4.Open Loop system are more stable. | 4.In closed Loop system stability depends on system components. |
5.optimization is not possible | 5. optimization is possible |
6.These systems are not reliable. | They are more reliable |
|
|
|
F(t) = M1 d2/dt2x1+ B1 d/dt (x1-x2) + k1(x1-x2) Similarly, for M2we have
K1(x1-x2) + B1d/dt(x1-x2) = k2x2+M2d2/dt2+B2dx2/dt |
|
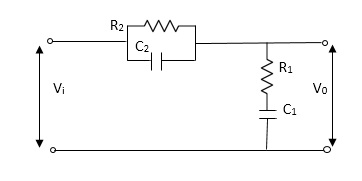
=R2*1/c2s/R2+1/c2s Z1= R2/1+R2c2s Let Z2 = R1+1/c1s Z2= 1+R1c1s/c1s V0(s)/vi(s) = z2/z1+z2 = 1+R1c1s/c1s/R2/1+R2c2s+1+R1c1s/c1s V0(s)/v0(s) =(c1+R1c1s) (1+R2c2s)/R2c1s+1+sR1c1s2R1R2c1c2 |
|
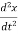 +B
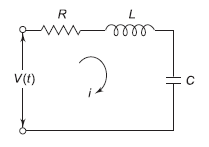
+B 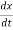 +kx (1) For series RLC circuit the mathematical equation is given as
+kx (1) For series RLC circuit the mathematical equation is given as
|
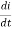 +
+ 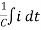 i =
i = 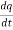 V(t) = L
V(t) = L  + R
+ R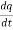 +
+  (2)Comparing 1 and 2 we see that
(2)Comparing 1 and 2 we see that F(t) v(t)
F(t) v(t) x q
x q M L
M L B R
B R i
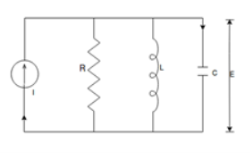
i 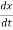 Q6) Explain force-current analogy?A6) For parallel RLC circuit shown below the KCL equation is written as
Q6) Explain force-current analogy?A6) For parallel RLC circuit shown below the KCL equation is written as
|
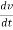 +
+  +
+ 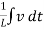 v =
v = 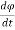 i(t) = C
i(t) = C 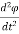 + R
+ R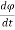 +
+  (3) Comparing 1 and 3 we find that
(3) Comparing 1 and 3 we find that F(t) i(t)
F(t) i(t)  M C
M C  x
x 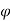
 B 1/R
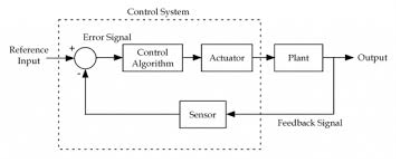
B 1/R  k 1/L Q7) What is friction and how it is useful for physical systems?A7) The friction exists in physical systems whenever mechanical surfaces are operated in sliding contact. The friction can bei) Coulomb Friction Force: This is the force of sliding friction between dry surface and is normally constant.ii) Viscous Friction Force: The force between a ansid body and a fluid medium is called as viscous friction force.iii) Stiction: The force required to initiate motion between two contacting surfaces. The frictional force acts in opposite direction to that of velocity. Sometimes friction is necessary in the physical system in order to improve the dynamic response of the system. Q8) What are feedforward and tracking systems?A8)Feedforward System:The feedback system is which work to reduce the error it’s the system. In some system where the disturbances input can be provided beforehand, its effect can be eliminated by feedforward system. Tracking System:The main objective of such system is to trace any particular location as direction of a targeted value on continuous basic. The basic examples of tracking, Range tracking, Tracking in phased array radars. Q9) What are control systems explain with block diagram?A9) A control system is a set of mechanical or electronic devices which control the other devices. In control system behaviours of the system is desired by differential equation.
k 1/L Q7) What is friction and how it is useful for physical systems?A7) The friction exists in physical systems whenever mechanical surfaces are operated in sliding contact. The friction can bei) Coulomb Friction Force: This is the force of sliding friction between dry surface and is normally constant.ii) Viscous Friction Force: The force between a ansid body and a fluid medium is called as viscous friction force.iii) Stiction: The force required to initiate motion between two contacting surfaces. The frictional force acts in opposite direction to that of velocity. Sometimes friction is necessary in the physical system in order to improve the dynamic response of the system. Q8) What are feedforward and tracking systems?A8)Feedforward System:The feedback system is which work to reduce the error it’s the system. In some system where the disturbances input can be provided beforehand, its effect can be eliminated by feedforward system. Tracking System:The main objective of such system is to trace any particular location as direction of a targeted value on continuous basic. The basic examples of tracking, Range tracking, Tracking in phased array radars. Q9) What are control systems explain with block diagram?A9) A control system is a set of mechanical or electronic devices which control the other devices. In control system behaviours of the system is desired by differential equation.
|
|