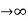The transfer function can be represented by the ratio of two polynomials G (S) = a0sn+a1 sn-1-------+an/b0sm+b1sm-1+-----+bn a0—an ---- constants
G(S) = K(s+z1) (s+z2) (as2+bs+c)/(S+A) (s+p2) (As2+Bs +c) K= a0/b0 (Gain of system) For poles –They are the values of s for which G(S) (S+p1)(S+p2)(A S= p1, -p2 , -B± For ZEROS – They are the values of s for which G(S) S=-z1, -z2 , -b± |











|
|
|

|
|
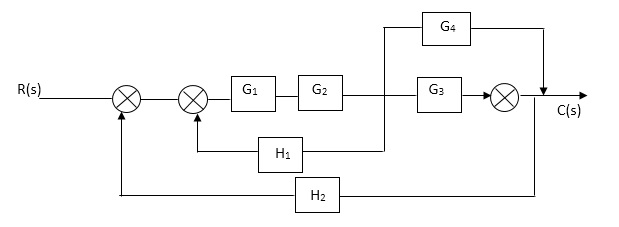
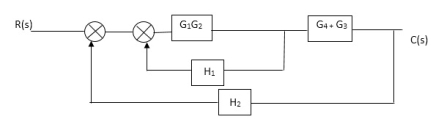
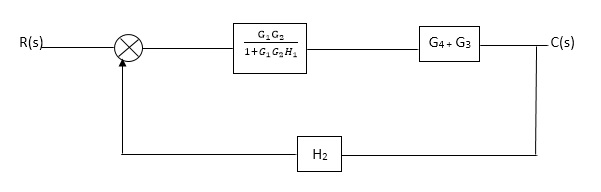
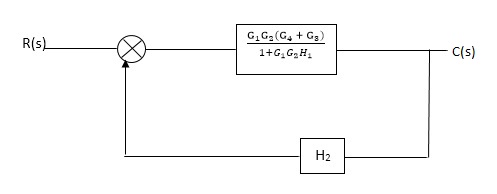
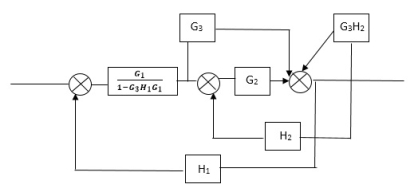
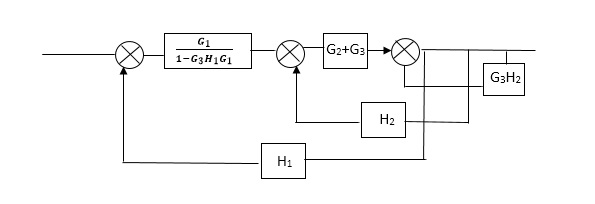
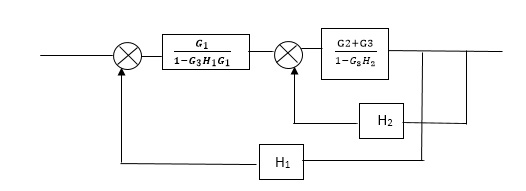
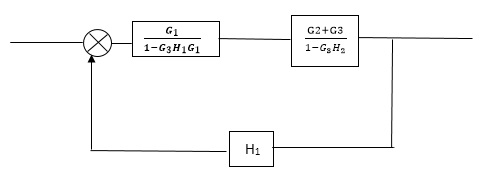
C(S)/R(S) = (G1G2) (G3+G4)/1+G1G2H1)/1-G1, G2(G3+G4) H2/1+G1G2H1 = G1G2(G3+G4)/1+G1G2H1-G1G2H2(G3+G4) =G1G2(G3+G4)/1+(H1-H2) (G1G2) (G3+G4) C(s)/R(S) = G1G2(G3+G4)/1+(H1-H2(G3+G4)) G1 G2 |


















 A3)
A3)
|
|
|
|






|



|



|
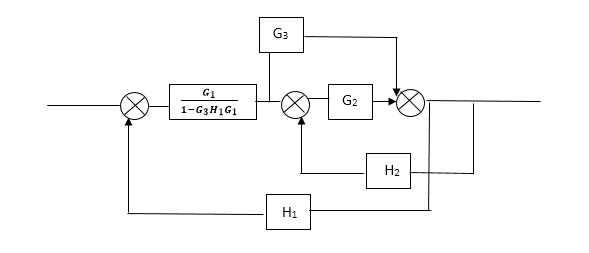
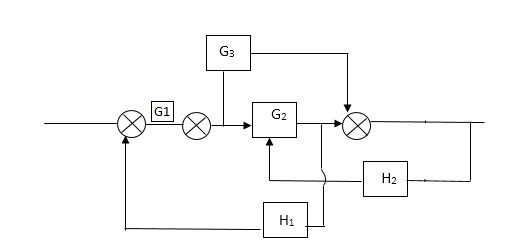
C(s)/R(s)= G1(G3+G2)/(1-G1G3X1) (1-G2X2) H1 = G(G3+G2)/(1-G3G1H1) (1-G2H2) + G1H1(G3+G2) = G1(G3+G2)/1-G3G1H1-G2H2+G1H1(G3+G2H1 =G1(G3+G2)/1-G3H2+G1G2H1(1+G3H2) |
|
|
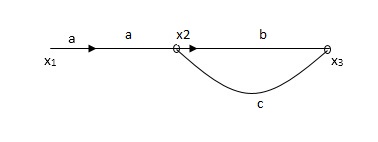
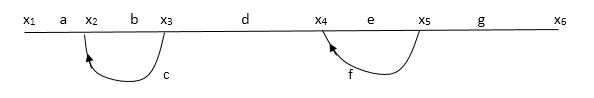
X1: - I/p node x2, x3, x4, x5, Qnlexmedili node X0:- o/p node abdeg:- forward path bc, ef :- Loop [iAnsated] x2 = ax1+c x3 x3= bx2 x4 = d x3+f x5 x5 = e x4 x6= g x5 x6 = g (e x4) = ge [dx3+ e f x5] xb = ge [d (bx2) + f (e x4)] xb = ge [ db (ax1+cx3) + fe (dx3+ fx5)] xb = ge [db (ax1+cb (ax1+x3) +fe[cdbx2]+ f(e [db (ax1+ cx3) x2 = ax1 + cb (x2) x4 = d bx2 + f exq x2 = ax1 + cbx2 = db (d4) + fe/1-cb x2 = ax1/(1-cb) xy = db x2 + f x6/g xy = db [ax1]/1-cb + f xb/g
x5 = c db (ax1)/1-cb + efxb/g xb = gx5 = gedb (ax1)/1-cb + g efxb/g Xb = gx5 gedb (ax1)/1-cb + g efxb/g (1- gef/g) xb = gedb ax1/1-ab Xb/x1 = gedb a/ (1- ef – bc + beef Xb/x1 = p/ 1- (L1+L2) + L1 L2 for iAnsated loops
|