MICRO
Unit-38051 Programming Q1) What are Assembler directives?Assembler directives are instructions to the assembler to perform various bookkeeping tasks, storage reservation, and other control functions. Q2) Explain the assembler directives of 8051? ORG (origin) The ORG directive is used to indicate the beginning of the address. The number that comes after ORG can be either in hex or in decimal. If the number is not followed by H, it is decimal and the assembler will convert it to hex. EQU (equate)This is used to define a constant without occupying a memory location. The following uses EQU for the counter constant and then the constant is used to load the R3 register. CONST EQU 25H
MOV A,#CONST ;COPY 25 INTO A
END
This indicates to the assembler the end of the source (asm) file. The END directive is the last line of an 8051 program, meaning that in the source code anything after the END directive is ignored by the assembler. Q3) Explain Assembly Language Program? The assembly language is a fully hardware related programming language. The embedded designers must have sufficient knowledge on hardware of particular processor or controllers before writing the program. The assembly language is developed by mnemonics.
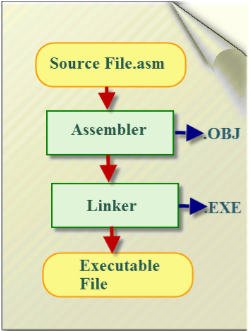
8051 Programming in Assembly LanguageAssembly programming language is developed by various compilers and the “keiluvison” is best suitable for microcontroller programming development. Microcontrollers or processors can understand only binary language in the form of ‘0s or 1s’; An assembler converts the assembly language to binary language, and then stores it in the microcontroller memory to perform the specific task. 8051 Microcontroller Programs in Assembly LanguageThe assembly language is made up of elements which all are used to write the program in a sequential manner. The rules should be followed to write programming in assembly language. Rules of Assembly LanguageThe assembly code must be written in upper case letters The labels must be followed by a colon . All symbols and labels must begin with a letter All comments are typed in lower case The last line of the program must be the END directive The assembly language mnemonics are in the form of op-code, such as MOV, ADD, JMP, and so on, which are used to perform the operations.
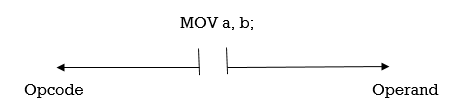
Op-code: The op-code is a single instruction that can be executed by the CPU. Here the op-code is a MOV instruction.Operands: The operands are a single piece of data that can be operated by the op-code. Example, multiplication operation is performed by the operands that are multiplied by the operand.Syntax: MUL a,b; Q4) Write a program to transfer the block of data from 20h to 30h to external location 1020h to 1030h. Mov r7, #0Ah ; initialize counter by 10d Mov r0, #20h ; get initial source location Mov dptr, #1020h ; get initial destination location Nxt: Mov a, @r0 ; get first content in acc Movx @dptr, a ; move it to external location Inc r0 ; increment source location Inc dptr ; increase destination locationDjnz r7, nxt ; decrease r7. if zero then over otherwise move next Q5) Write A Program to toggle the PORT1 LEDsORG 0000H
TOGLE: MOV P1, #01 //move 00000001 to the p1 register//
CALL DELAY //execute the delay//
MOV A, P1 //move p1 value to the accumulator//
CPL A //complement A value //
MOV P1, A //move 11111110 to the port1 register//
CALL DELAY //execute the delay//
SJMP TOGLE
DELAY: MOV R5, #10H //load register R5 with 10//
TWO: MOV R6, #200 //load register R6 with 200//
ONE: MOV R7, #200 //load register R7 with 200//
DJNZ R7, $ //decrement R7 till it is zero//
DJNZ R6, ONE //decrement R7 till it is zero//
DJNZ R5, TWO //decrement R7 till it is zero//
RET //go back to the main program //
END Q6) Write a program to calculate the 500us time delay.MOV TMOD, #10H //select the timer mode by the registers//
MOV TH1, #0FEH // store the delay time in higher bit//
MOV TL1, #32H // store the delay time in low bit//
JNB TF1, $ //decrement the value of the timer till it is zero//
CLR TF1 //clear the timer flag bit//
CLR TR1 //OFF the timer// Q7) WAP to count the 250 pulses using mode0 count0 ORG 0000H
MOV TMOD, #50H //select the counter//
MOV TH0, #15 //move the counting pulses higher bit//
MOV TH1, #9FH //move the counting pulses, lower bit//
SET TR0 //ON the timer//
JNB $ //decrement the count value till zero//
CLR TF0 //clear the counter, flag bit//
CLR TR0 //stop the timer//
END Q8) Write a program to add two numbers?ORG 0H ;start at location 0 MOV R5,#25H ;load 25H into R5MOV R7,#34H ;load 34H into R7 MOV A,#0 ;load 0 into A ADD A,R5 ;add contents of R5 to A = A + R5 ADD A,R7 ;add contents of R7 to A ADD A,#12H ;add to A value 12H HERE:SJMP HERE ;stay in this loop END ;end of asm source file Q9) Write a program to multiply two numbers?MOV R0, #20H;set source address 20H to R0 MOV R1, #30H;set destination address 30H to R1 MOV A, @R0;take the first operand from source to register A INCR0; Point to the next location MOV B,@R0;take the second operand from source to register B MUL AB ;Multiply A and B MOV @R1, B; Store higher order byte to 30H INC R1; Increase R1 to point to the next location MOV @R1, A;Store lower order byte to 31HHALT: SJMP HALT ; Stop the program Q10) Write a program to divide two numbers?MOV R0, #20H;set source address 20H to R0MOV R1, #30H;set destination address 30H to R1MOV A, @R0;take the first operand from source to register AINC R0; Point to the next locationMOV B, @R0; take the second operand from source to register BDIV AB ; Divide A by BMOV @R1, A; Store Quotient to 30HINC R1; Increase R1 to point to the next locationMOV @R1, B; Store Remainder to 31HHALT: SJMP HALT ;Stop the program
MOV A,#CONST ;COPY 25 INTO A
END
|
|
TOGLE: MOV P1, #01 //move 00000001 to the p1 register//
CALL DELAY //execute the delay//
MOV A, P1 //move p1 value to the accumulator//
CPL A //complement A value //
MOV P1, A //move 11111110 to the port1 register//
CALL DELAY //execute the delay//
SJMP TOGLE
DELAY: MOV R5, #10H //load register R5 with 10//
TWO: MOV R6, #200 //load register R6 with 200//
ONE: MOV R7, #200 //load register R7 with 200//
DJNZ R7, $ //decrement R7 till it is zero//
DJNZ R6, ONE //decrement R7 till it is zero//
DJNZ R5, TWO //decrement R7 till it is zero//
RET //go back to the main program //
END Q6) Write a program to calculate the 500us time delay.MOV TMOD, #10H //select the timer mode by the registers//
MOV TH1, #0FEH // store the delay time in higher bit//
MOV TL1, #32H // store the delay time in low bit//
JNB TF1, $ //decrement the value of the timer till it is zero//
CLR TF1 //clear the timer flag bit//
CLR TR1 //OFF the timer// Q7) WAP to count the 250 pulses using mode0 count0 ORG 0000H
MOV TMOD, #50H //select the counter//
MOV TH0, #15 //move the counting pulses higher bit//
MOV TH1, #9FH //move the counting pulses, lower bit//
SET TR0 //ON the timer//
JNB $ //decrement the count value till zero//
CLR TF0 //clear the counter, flag bit//
CLR TR0 //stop the timer//
END Q8) Write a program to add two numbers?ORG 0H ;start at location 0 MOV R5,#25H ;load 25H into R5MOV R7,#34H ;load 34H into R7 MOV A,#0 ;load 0 into A ADD A,R5 ;add contents of R5 to A = A + R5 ADD A,R7 ;add contents of R7 to A ADD A,#12H ;add to A value 12H HERE:SJMP HERE ;stay in this loop END ;end of asm source file Q9) Write a program to multiply two numbers?MOV R0, #20H;set source address 20H to R0 MOV R1, #30H;set destination address 30H to R1 MOV A, @R0;take the first operand from source to register A INCR0; Point to the next location MOV B,@R0;take the second operand from source to register B MUL AB ;Multiply A and B MOV @R1, B; Store higher order byte to 30H INC R1; Increase R1 to point to the next location MOV @R1, A;Store lower order byte to 31HHALT: SJMP HALT ; Stop the program Q10) Write a program to divide two numbers?MOV R0, #20H;set source address 20H to R0MOV R1, #30H;set destination address 30H to R1MOV A, @R0;take the first operand from source to register AINC R0; Point to the next locationMOV B, @R0; take the second operand from source to register BDIV AB ; Divide A by BMOV @R1, A; Store Quotient to 30HINC R1; Increase R1 to point to the next locationMOV @R1, B; Store Remainder to 31HHALT: SJMP HALT ;Stop the program
0 matching results found