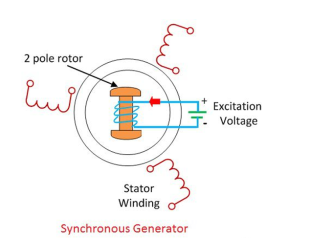
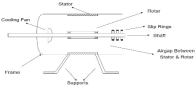
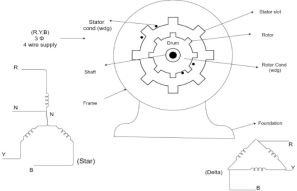
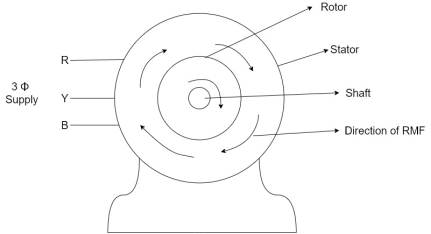
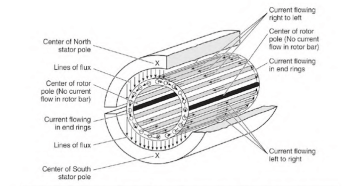
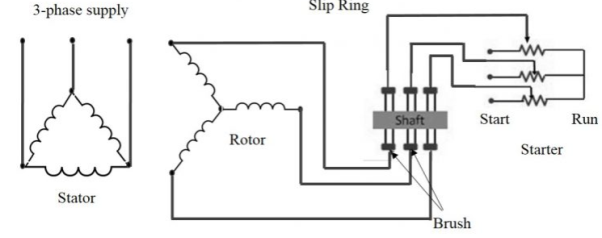
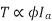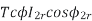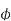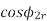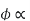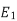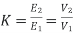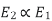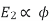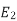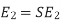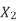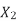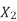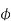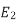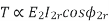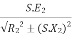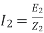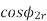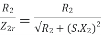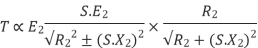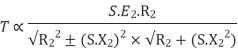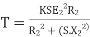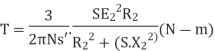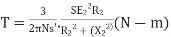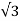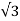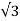|
|
|
|
|
|
r = Smax. X —— (I) |
r+R= (Smax)’. X —— (ii) |
From equation (i) and (ii), R = r(S’ max/Smax – 1) —— (iii) By definition of Smax, we get Smax = 1 – (Nmax/Ns) —— (iv) Putting S’max =1 in equation (iii), we get | ||
R = r. (1/Smax-1) —— (v) Let’s say, Ns = synchronous speed of 1000rpm and pull-out torque happens at 900 rpm, equation (iv) reduces to Smax = 0.1 (i.e., 10% slip) Substitute in equation (v), R = r. (1/0.1 – 1) | ||
R = 9. r | ||
We can mathematically say that,
But in case of induction motor Suffix 1 -> used for stator/stator parts (qty) Suffix 2-> used for rotor/rotor parts(qty)
Therefore,
But, | ||||
Transformation ratio i.e. given by Therefore,
And also Hence i.e.
4 Substract (3) and (4) into (1) equation we get,
| ||||
At starting condition slip S=1 So, | ||||
9. A three phase 15hp,460V , 4-pole 60 Hz 1728 rpm induction motor delivers full output power to the load connected to its shaft. The wind age and friction loss of the motor is 750 W. Determine the
Full load shaft power = Pout = 15.746 Mechanical power = Pm = Pout + ∆ Pm = 11190 + 750 = 11940 W Air gap power Pavg = Pm / 1-s Ns = 120.6/4 = 1800 rpm S = ns – n /ns = 1800 – 1728 /1800 =0.04 Pag = 11940/1-0.04 = 12.437.5 W Rotor copper loss ∆Pα = 0.04 x 12.437.5 = 497.5 W |
Mativa) |Ia f.l| = S rated/ V rated = 10 x 10 3/ 230/ | ||
25.1 < -36.87 E = Vt + Ia(Ra + jXs) = 230<0/ = 161.7 < 5.8 V ꙴ = |E| - |Vt|/ |Vt| = 161.7 – 230/
b) Ia = 25.1 < 36.87 A
E = 230/ | ||